Chemicals and chemical products are generally classified in Section VI – Products of the Chemical or Allied Industries, of the HS Nomenclature:
| SECTION VI – PRODUCTS OF THE CHEMICAL OR ALLIED INDUSTRIES | |
| Chapter 28 | Inorganic chemicals; organic or inorganic compounds of precious metals, of rare-earth metals, of radioactive elements or of isotopes |
     |
|
| Chapter 29 | Organic chemicals |
    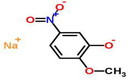 |
|
| Chapter 30 | Pharmaceutical products |
     |
|
| Chapter 31 | Fertilisers |
     |
|
| Chapter 32 | Tanning or dyeing extracts; tannins and their derivatives; dyes, pigments and other colouring matter; paints and varnishes; putty and other mastics; inks |
     |
|
| Chapter 33 | Essential oils and resinoids; perfumery, cosmetic or toilet preparations |
     |
|
| Chapter 34 | Soap, organic surface-active agents, washing preparations, lubricating preparations, artificial waxes, prepared waxes, polishing or scouring preparations, candles and similar articles, modelling pastes, “dental waxes” and dental preparations with a basis of plaster |
     |
|
| Chapter 35 | Albuminoidal substances; modified starches; glues; enzymes |
     |
|
| Chapter 36 | Explosives; pyrotechnic products; matches; pyrophoric alloys; certain combustible preparations |
     |
|
| Chapter 37 | Photographic or cinematographic goods |
     |
|
| Chapter 38 | Miscellaneous chemical products |
     |
|
Table of Contents
PRODUCTS OF THE CHEMICAL OR ALLIED INDUSTRIES
Source:European Union Website
Scope of Section VI
This Section covers inorganic and organic chemicals and miscellaneous chemical products
of Chapters 28 to 38.
This Section does not include products that are excluded from the Section by the virtue
of Notes to each Chapter, for example, yeast (Chapter 21), mixtures of chemicals with
foodstuffs or other substances with nutritive value, of a kind used in the preparation of
certain human foodstuffs (for example, improvers for pastry, biscuits, cakes, and other
bakers’ wares) (mainly Chapter 21), ethyl alcohol (Chapter 22), sodium chloride (Chapter
25), methane and propane (Chapter 27), optical goods (Chapter 90).
How to Classify Chemicals and Chemical Products
The GIRs provide a step-by-step basis for the classification of goods and ensure
uniform interpretation of the HS nomenclature.
As a general guide, you would need to first
understand your product before you can identify the possible HS Chapters and Headings.
Once the possible HS Chapters and Headings are identified, check and apply the relevant
Section Notes, Chapters Notes and Subheading Notes to obtain the 4-digit HS heading.
In every case, the goods must first be classified in the appropriate 4-digit HS heading,
followed by the appropriate 1-dash subheading, and the appropriate 2-dash subheading
within the selected 1-dash subheading and so on, till the 8-digit HS code is obtained.
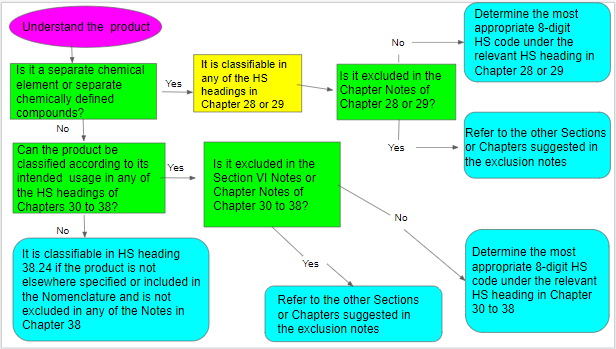
Step1.Understand your product
To classify chemicals and chemicals products, you would need to understand the
following:
- Is it a separate chemical element, a separate chemically defined compound, or a chemical mixture?
A separate chemically defined compound is a substance that consists of one molecular species (e.g., covalent or ionic) whose composition is defined by a constant ratio of elements and can be represented by a definitive structural diagram. In a crystal lattice, the molecular species corresponds to the repeating unit. - What are the function, intended usage, and chemical composition of the product?
- How do the individual chemical components in the product contribute to the function and intended usage?
Step2.Identify possible Chapters and Headings
Identify the possible chapters and headings based on the chemical composition, function, and intended usage of the product.
Separate Chemical Elements and Separate Chemically Defined Compounds
Separate chemical elements and separate chemically defined compounds
(commonly known as pure chemicals) are generally classified in Chapters 28 and 29,
depending on whether they are inorganic or organic chemicals. Such chemical elements or
compounds, whether or not containing impurities, would remain classified in these
Chapters, and could still be classifiable in their respective Chapters when they are mixed
with certain substances, provided such additions do not render the product particularly
suitable for a specific use.
| CHAPTER 28 | CHAPTER 29 |
| Inorganic compounds | Organic compounds |
| Chemical elements | Hydrocarbons |
| Oxides | Derivatives |
| Hydroxides, Inorganic acids Inorganic salts |
Heterocyclic compounds Apart from carbon they may also contain N, O, S… |
| Generally soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents | Generally insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents |
The presence of by-products or unconverted starting materials as a result of the
the manufacturing process of a chemical product of Chapter 28 or 29 could be regarded as
permissible impurities. The chemical product could still be classified in Chapter 28 or 29
provided that these impurities are not deliberately left in the product to render it suitable
for a specific use.
*Note: If the product is a plastic product, it is possible to be classified in Chapter 39 of Section VII.
Refer to Chapter Notes of Chapter 39 to check if the product is classifiable under that Chapter
Chemical Mixture
Chemical mixtures are generally classified in Chapters 30 to 38 based on their
intended usage. You should shortlist the possible HS headings according to the intended
usage of your product.
Step3.Apply the relevant Section Notes,
Chapter Notes and Subheading Notes
Examine and apply the Section Notes, Chapter Notes and Subheading Notes of all the
identified possible HS headings for the product, in order to identify the most appropriate HS heading.
The Notes will state the following:
- Definitions and clarifications of certain terms and products
- Classification of certain products in a specific heading that takes precedence over
other headings of the Section or the Nomenclature - Scope of products in specific chapters, headings and subheadings by excluding or
including certain group(s) of products
With reference to Note 1 of Chapter 28 and 29, other than separate chemical
elements and separate chemically defined compounds (whether or not containing
impurities), your chemical product can be classifiable under Chapter 28 or 29 if:
- The product is dissolved in water;
- The product is dissolved in other solvents provided the solution constitutes a
normal and necessary method of putting up these products solely for reasons of
safety or for transport - The product contains an added stabiliser (including an anti-caking agent) for
preservation or transport - The product contains an added anti-dusting agent or a colouring substance to
facilitate their identification or for safety reasons, provided that the additions do
not render the product particularly useful for specific use rather than for general
use.
However, certain separate chemical elements and chemically defined compounds
are excluded from Chapter 28 and 29 and are classifiable in other Chapters of the
nomenclature. For example, certain separate chemically defined compounds are classified in
Chapter 31 (Fertilisers) by Note 3c to Chapter 28 and Note 2f to Chapter 29, even when
they are clearly not used as fertilizers.
*Note: If the product is radioactive, a stable isotope or compound of stable isotope or is related to
precious metals or compounds of rare-earth metals, yttrium, scandium or of mercury, please refer to
Note 1 of Section VI.
Step4.Determine the HS code at 8-digit level
Once the most appropriate HS heading for your product has been identified,
compare the HS subheadings within the HS heading to obtain the relevant HS code for your
product. Start by comparing the 1-dash descriptions to find the most suitable one. If there is
a subsequent breakdown for the 1-dash descriptions, proceed to compare and select the
most appropriate 2-dash description under that 1-dash description. Repeat the process if
there are further breakdowns under the 2-dash description until you obtain the most
appropriate 8-digit HS code for the product.
Summary Flowchart on how to classify chemicals
Case studies
Case Study 1 – Hydrogen peroxide
The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) of hydrogen peroxide indicates the chemical composition as follows:
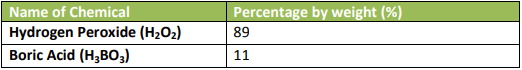
The chemical is presented in liquid form.
Step 1.Understand your product.
The MSDS is for hydrogen peroxide. However, boric acid is also present in the
composition. The function of the boric acid is to stabilize hydrogen peroxide for
preservation.
Step 2,3.Identify possible Chapters and Headings and apply the relevant Section Notes, Chapter Notes and Subheading Notes.
Based on the information of the product, it is a chemically defined compound with
an added stabiliser. Therefore, hydrogen peroxide can be classified in Chapter 28 based on
the terms of the heading and the relative section and chapter notes (Note 1 (d) to Chapter
28). The notes to Chapter 28 include the product to be classified in Chapter 28:

Step 4.Determine the HS code at 8-digit level
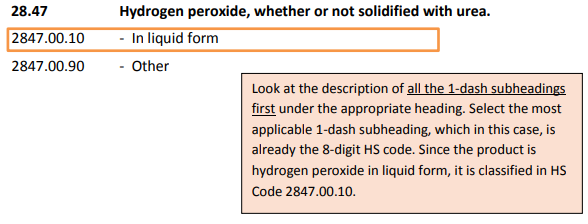
*Singapore customs tariff
Case Study 2 – Camping fuel
The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) of a camping fuel indicates the chemical composition as follows:
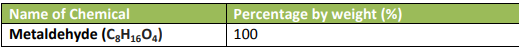
The chemical product is put up in tablet form for use as fuels for camping stoves.
Step 1.Understand your product.
The product contains 100% metaldehyde, and it is a separate chemically defined
compound. It is a type of camping fuel in tablet form.
Step 2,3.Identify possible Chapters and Headings and apply the relevant Section Notes, Chapter Notes and Subheading Notes.
It is possible for the product to be classifiable in Chapter 29 (as a separate chemically
defined compound) and in Chapter 36 as a combustible preparation. However, Note 2(ij) to
Chapter 29 excludes the product to be classified in Chapter 29 and Note 1 and 2 (a) to
Chapter 36 includes the product to be classified in Chapter 36. Therefore, the product is to
be classified in Chapter 36, HS heading 36.06.


Step 4.Determine the HS code at 8-digit level


*Singapore customs tariff
Case Study 3 – Insecticide
The Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) of the insecticide indicates the chemical composition as follows:
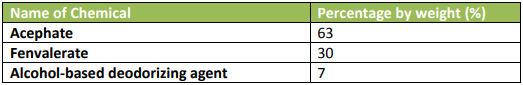
The chemical product functions as an insecticide, to exterminate aphids in
vegetables. The product is presented in aerosol spray containers, packed for retail sale.
Step 1.Understand your product.
The chemical product is a type of insecticide with a mixture of different chemicals,
each serving different function. The chemical composition renders the product particularly
suitable for a specific use, that is, an insecticide.
Step 2.Identify possible Chapters and Headings.
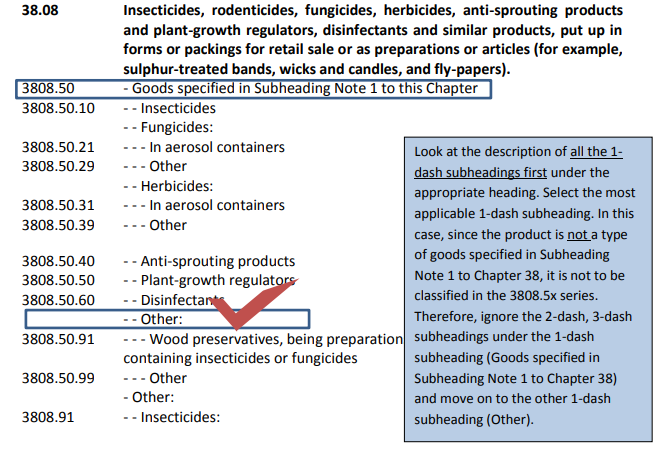
As it is an insecticide, it can be classified in Section VI HS heading 38.08.
Step 3.Apply the relevant Section Notes, Chapter Notes and Subheading Notes.
The Subheading Note 1 in Chapter 38 listed out the goods covered under the HS Subheading 3808.50.
Step 4.Determine the HS code at 8-digit level
To start, compare the descriptions of 1 dash subheadings under the appropriate
heading and choose the correct 1 dash. Next, repeat the process for the subsequent lines
with 2 or more dashes.

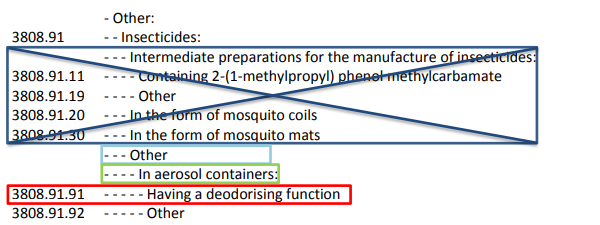 *Singapore customs tariff
*Singapore customs tariff
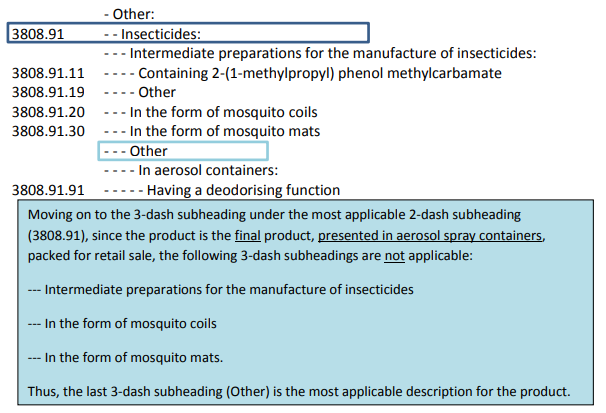
Moving on to the 4-dash subheading under the most applicable 3-dash subheading (Other),
since the product is presented in aerosol spray containers, packed for retail sale, the 4-dash
subheading description “In aerosol containers” is the most applicable description.
Moving on to the 5-dash subheading under the most applicable 4-dash subheading (In
aerosol containers), since the product contains deodorizing agents, it is most appropriate to
be classified in the 5-dash subheading (Having a deodorizing function).
Thus, the product is classified in HS Code 3808.91.91. in the case of Singapore customs tariff.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1) I have a 10-digit HS code provided by my overseas supplier for their chemical
product. Can I use the first 8-digit for import into my country?
The HS is internationally harmonized only at the 6-digit level. You may use the HS
code provided by your overseas supplier as a reference and determine the 8-digit HS
code which is most appropriate and applicable to your product from the import country version of the HS code.
Q2) What information do I need to determine the HS code of chemical products?
To determine the HS code, you may need the following information:
-
- chemical composition adding up to 100%
- chemical structure
- product usage
- form (i.e. powder, liquid)
The information could be found in the product catalogue/brochure or the product’s
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS).
Q3) Can I determine the HS code of a chemical product using its CAS Registry Number?
Chemical Abstracts Service Registry Number (CAS RN) is a unique number tagged to
a chemical by the American Chemical Society and is used internationally to identify
chemicals. For chemicals with CAS RN.
However, since the list is not exhaustive, you may also refer to the Europa website for assistance.
Do note that the Europa website is meant as a guide and
traders are advised to make reference to the import Customs publication for the 8-digit HS code.
The next alternative is to research on the chemical structure and its functionality of
the chemical in the web, and determine the most appropriate HS code.
Q4) Is there a specific HS heading for washing preparations for cleaning industrial machines?
If the washing preparation is in the form of bar, cake, moulded piece or shape, they
would be classified in HS heading 34.01. Otherwise, it would be classified under HS
heading 34.02 if it is in other forms (e.g. liquid, pastes, etc.) not specified in HS
heading 34.01.
Resources:Guidebook on the HS Classification of Chemicals & Chemical Products
Details of Chemical Headings
Chapter 28 Inorganic Chemicals
Inorganic Chemicals; Organic or Inorganic Compounds of
Precious Metals, of Rare-Earth Metals, of Radioactive Elements or of Isotopes
This Chapter covers, in principle, separate chemical elements and separate chemically
defined compounds, subject to the provision of the legal notes.
As specified in Note 2 to the Chapter, certain compounds containing carbon in their
structures are to be classified in Chapter 28 as inorganic compounds, such as oxides of
carbon, Calcium carbonate.
Separate chemical elements and separate chemically defined compounds containing
impurities, or dissolved in water, remain classified in Chapter 28.
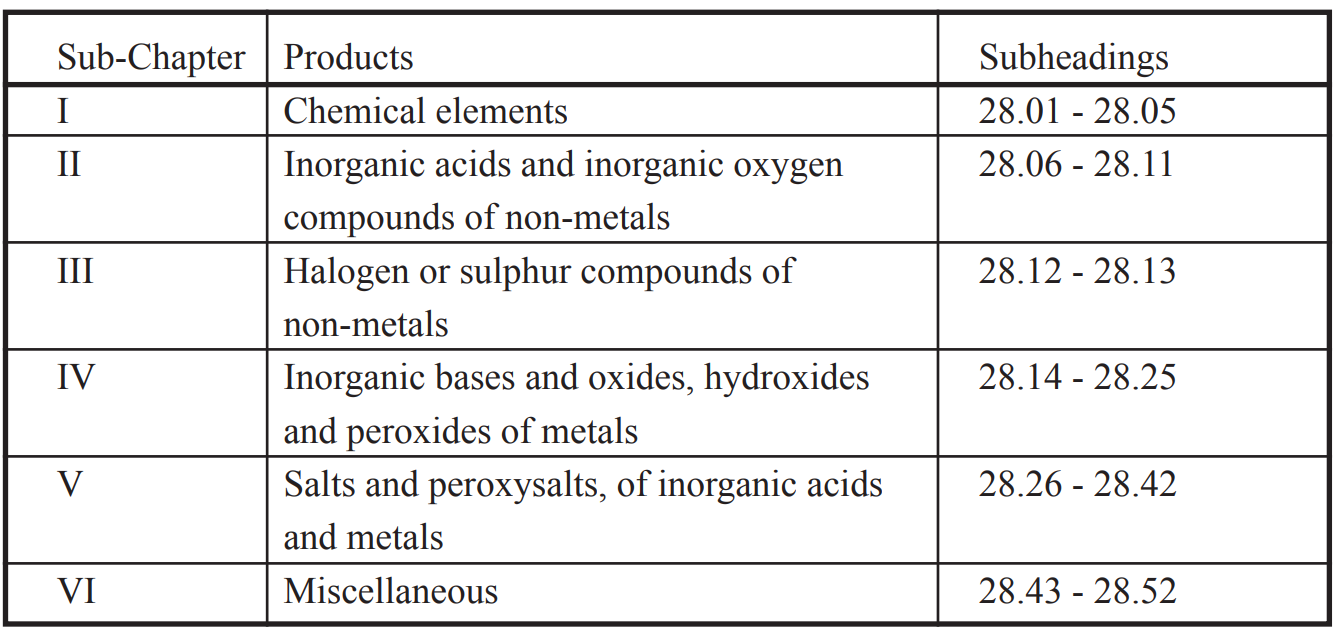
Chapter 28 is categorized into six groups as shown below:
For purposes of transportation and preservation, Separate chemically defined elements
and compounds put up with an added stabilizer remain classified in this Chapter. Products
added to certain chemicals to keep them in their original physical state are also to be
regarded as stabilizers, provided that the addition does not alter the character of the basic
product and render it particularly suitable for specific use rather than for general use.
Example;
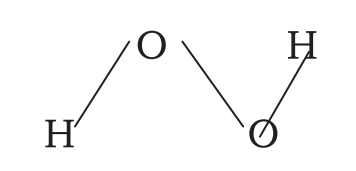
Stabilized by the addition of Boric acid remains classified in Heading 28.47.
Hydrogen Peroxide
• Hydrogen peroxide (28.47) stabilized by additional of boric acid remain classified
in this Chapter because is of a type normally used for the purpose.
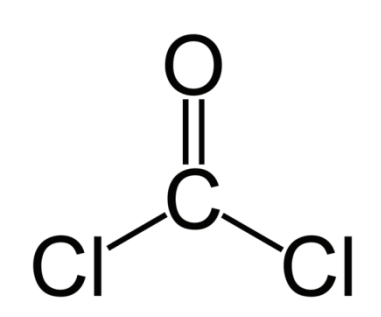
• Carbonyl Chloride dissolved in Toluene or Benzene is classified in heading
38.24.
• Carbonyl chloride (subheading 2812.11) dissolved in benzene cannot remain
classified in this chapter because the dilution is not necessary for transportation
and render the product suitable for specific usage.
The scope of priority heading 28.52, compounds of mercury, is expanded to include
the same whether or not chemically defined. 2852.10 (chemically defined inorganic or
organic compound of mercury). Non-chemically compound of mercury fall under sub
heading 2852.90.
This subdivision was done for purposes of capturing data on certain hazardous chemicals
and pesticides as measures to facilitate the monitoring and control in international trade.
Relationship with other parts of the Nomenclature
Subject to the provision of the legal notes 3 and 8 to Chapter 28, the following chemically
defined inorganic compounds are excluded from Chapter 28 and classified in other
Chapters, for example, Sodium chloride in Chapter 25, Ammonium nitrate in Chapter 31,
Precious stones in Chapter 71, Artificial graphite in Heading 38.01
Chapter 29 Organic Chemicals
Organic Chemicals
Each Heading has a link to structural formula categorized by Heading by Japanese Customs.
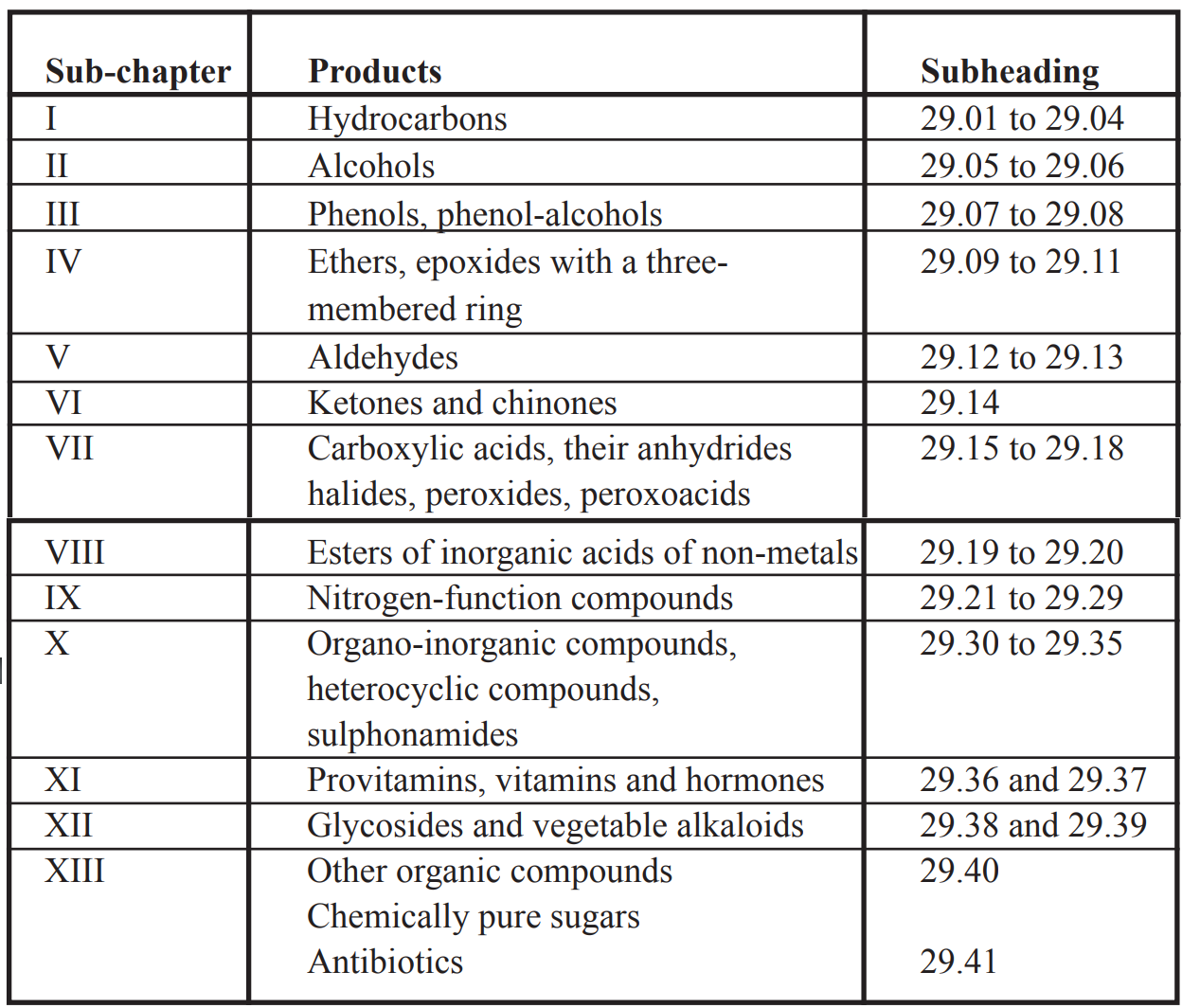
| S.C.1 | HYDROCARBONS AND THEIR HALOGENATED, SULPHONATED, NITRATED OR NITROSATED DERIVATIVES |
|
| 29.01 | Acyclic hydrocarbons | |
    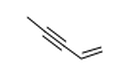 |
||
| 29.02 | Cyclic hydrocarbons | |
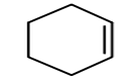 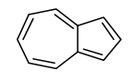 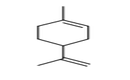   |
||
| 29.03 | Halogenated derivatives of hydrocarbons | |
  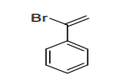 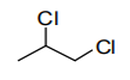 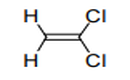 |
||
| 29.04 | – Sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives of hydrocarbons, whether or not halogenated | |
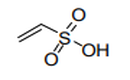     |
||
| S.C.2 | ALCOHOLS AND THEIR HALOGENATED, SULPHONATED,NITRATED OR NITROSATED DERIVATIVES | |
| 29.05 | Acyclic alcohols and their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
    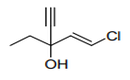 |
||
| 29.06 | Cyclic alcohols and their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
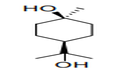 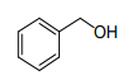 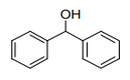 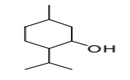 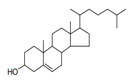 |
||
| S.C.3 | PHENOLS, PHENOL-ALCOHOLS, AND THEIR HALOGENATED, SULPHONATED, NITRATED OR NITROSATED DERIVATIVES |
|
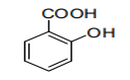
| 29.07 | Phenols; phenol-alcohols | |
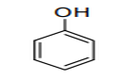 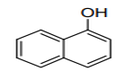 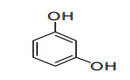 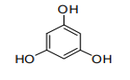 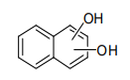 |
||
| 29.08 | Halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives of phenols or phenol- alcohols | |
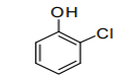     |
||
| S.C.4 | ETHERS, ALCOHOL PEROXIDES, ETHER PEROXIDES, KETONE PEROXIDES, EPOXIDES WITH A THREE-MEMBERED RING, ACETALS AND HEMIACETALS, AND THEIR HALOGENATED, SULPHONATED, NITRATED OR NITROSATED DERIVATIVES |
|
| 29.09 | Ethers, ether-alcohols, ether-phenols, ether-alcohol-phenols, alcohol peroxides, ether peroxides, ketone peroxides (whether or not chemically defined), and their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
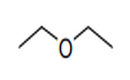 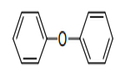 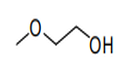 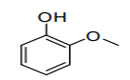 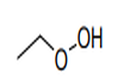 |
||
| 29.10 | Epoxides, epoxyalcohols, epoxyphenols and epoxyethers, with a three-membered ring, and their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
 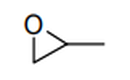 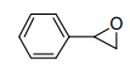 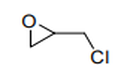 |
||
| 29.11 | Acetals and hemiacetals, whether or not with other oxygen function, and their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
     |
||
| S.C.5 | ALDEHYDE-FUNCTION COMPOUNDS | |
| 29.12 | Aldehydes, whether or not with other oxygen function; cyclic polymers of aldehydes; paraformaldehyde |
|
   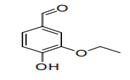 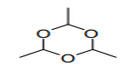 |
||
| 29.13 | Halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives of products of heading 29.12 |
|
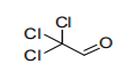 |
||
| S.C.6 | KETONE-FUNCTION COMPOUNDS AND QUINONE-FUNCTION COMPOUNDS | |
| 29.14 | Ketones and quinones, whether or not with other oxygen function, and their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
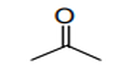 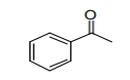 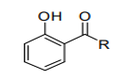 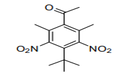 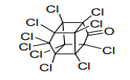 |
||
| S.C.7 | CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR ANHYDRIDES, HALIDES, PEROXIDES AND PEROXYACIDS AND THEIR HALOGENATED, SULPHONATED, NITRATED OR NITROSATED DERIVATIVES |
|
| 29.15 | Saturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
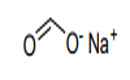 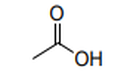 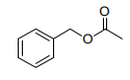 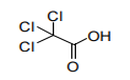 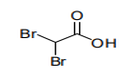 |
||
| 29.16 | Unsaturated acyclic monocarboxylic acids, cyclic monocarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
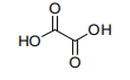
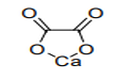
|
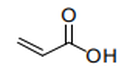 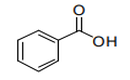 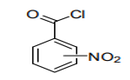   |
||
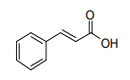
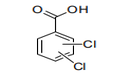
| 29.17 | Polycarboxylic acids, their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives | |
     |
||
| 29.18 | Carboxylic acids with additional oxygen function and their anhydrides, halides, peroxides and peroxyacids; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
     |
||
| S.C.8 | ESTERS OF INORGANIC ACIDS OF NON-METALS AND THEIR SALTS, AND THEIR HALOGENATED, SULPHONATED, NITRATED OR NITROSATED DERIVATIVES |
|
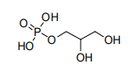
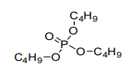
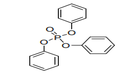
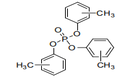
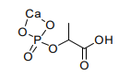
| 29.19 | Phosphoric esters and their salts, including lactophosphates; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
     |
||
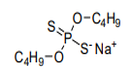
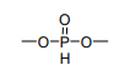
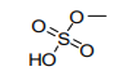
| 29.20 | Esters of other inorganic acids of non-metals (excluding esters of hydrogen halides) and their salts; their halogenated, sulphonated, nitrated or nitrosated derivatives |
|
     |
||
| S.C.9 | NITROGEN-FUNCTION COMPOUNDS | |
| 29.21 | Amine-function compounds (+) | |
     |
||
| 29.22 | Oxygen-function amino-compounds (+) | |
     |
||
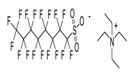
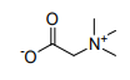
| 29.23 | Quaternary ammonium salts and hydroxides; lecithins and other phosphoaminolipids, whether or not chemically defined | |
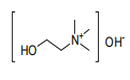  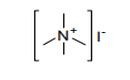   |
||
| 29.24 | Carboxyamide-function compounds; amide-function compounds of carbonic acid | |
     |
||
| 29.25 | Carboxyimide-function compounds (including saccharin and its salts) and iminefunction compounds | |
  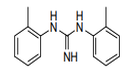 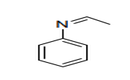 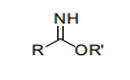 |
||
| 29.26 | Nitrile-function compounds | |
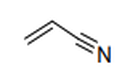     |
||
| 29.27 | Diazo-, azo- or azoxy-compounds | |
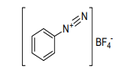 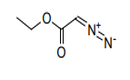 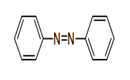 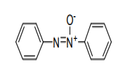 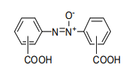 |
||
| 29.28 | Organic derivatives of hydrazine or of hydroxylamine | |
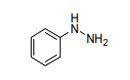 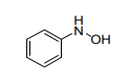 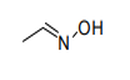   |
||
| 29.29 | Compounds with other nitrogen function | |
     |
||
| S.C.10 | ORGANO-INORGANIC COMPOUNDS, HETEROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS, NUCLEIC ACIDS AND THEIR SALTS, AND SULPHONAMIDES |
|
| 29.30 | Organo-sulphur compounds | |
 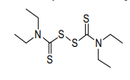 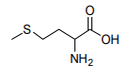 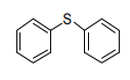 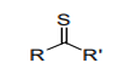 |
||
| 29.31 | Other organo-inorganic compounds | |
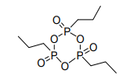 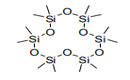 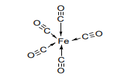 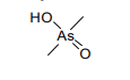  |
||
| 29.32 | Heterocyclic compounds with oxygen hetero-atom(s) only (+) | |
     |
||
| 29.33 | Heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only (+) | |
  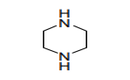 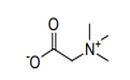 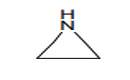 |
||
| 29.34 | Nucleic acids and their salts, whether or not chemically defined; other heterocyclic compounds |
|
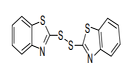 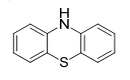 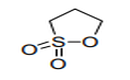 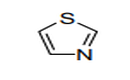 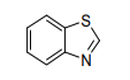 |
||
| 29.35 | Sulphonamides | |
    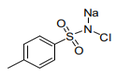 |
||
| S.C.11 | PROVITAMINS, VITAMINS AND HORMONES | |
| 29.36 | Provitamins and vitamins, natural or reproduced by synthesis (including natural concentrates), derivatives thereof used primarily as vitamins, and intermixtures of the foregoing, whether or not in any solvent (+) |
|
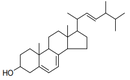 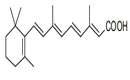 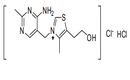 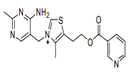 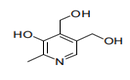 |
||
| 29.37 | Hormones, prostaglandins, thromboxanes and leukotrienes, natural or reproduced by synthesis; derivatives and structural analogues thereof, including chain modified polypeptides, used primarily as hormones.(+) |
|
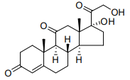 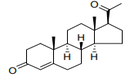    |
||
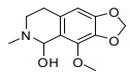
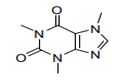
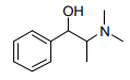
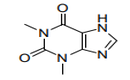
| S.C.12 | GLYCOSIDES AND ALKALOIDS, NATURAL OR REPRODUCED BY SYNTHESIS, AND THEIR SALTS, ETHERS, ESTERS AND OTHER DERIVATIVES |
|
| 29.38 | Glycosides, natural or reproduced by synthesis, and their salts, ethers, esters and other derivatives |
|
     |
||
| 29.39 | Alkaloids, natural or reproduced by synthesis, and their salts, ethers, esters and other derivatives |
|
     |
||
| S.C.13 | OTHER ORGANIC COMPOUNDS | |
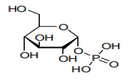
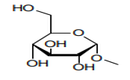
| 29.40 | Sugars, chemically pure, other than sucrose, lactose, maltose, glucose and fructose; sugar ethers, sugar acetals and sugar esters, and their salts, other than products of heading 29.37, 29.38 or 29.39. |
|
     |
||
| 29.41 | Antibiotics (+) | |
  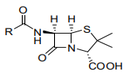 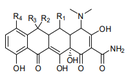  |
||
| 29.42 | Other organic compounds | |
Within any one heading of this Chapter, derivatives of a chemical compound (or group
of chemical compounds) are to be classified in the same subheading as that compound
(or group of compounds) provided that they are not more specifically covered by any
other subheading and that there is no residual subheading named “Other” in the series of
subheadings concerned (subheading note 1 to Chapter 29).
The Chapter is divided into 13 categories as shown below:
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover :
(a) Goods of heading 15.04 or crude glycerol of heading 15.20;
(b) Ethyl alcohol (heading 22.07 or 22.08);
(c) Methane or propane (heading 27.11);
(d) The compounds of carbon mentioned in Note 2 to Chapter 28;
(e) Urea (heading 31.02 or 31.05);
Items classified in this Chapter are mainly chemically defined organic compounds other
than those excluded in note 2 to Chapter 29, some as listed above.
Impurities and stabilizers present in chemicals of this Chapter have limitation as provided
in note 1 to Chapter 29 just as it is in Chapter 28. Presence of water in most cases however
has no effect (Note 1(d) to this Chapter).
There is also a danger of misclassifying other chemicals of this Chapter such as vitamins and
antibiotic since their classification can also be affected by level of purity as demonstrated
in Chapter 27, by presentation either in bulk or put up for retail or in measured doses, or
by being mixed with other materials of other Chapters for specific use.
Relationship with other parts of the Nomenclature
• Diary feed supplements containing antibiotic and vitamins for the wellbeing of
animals – 23.09
• Vitamins and mineral supplements preparation, edible, for people’s wellbeing
or maintaining health but which can not cure or prevent diseases – 21.06
• Vitamins put up in measured doses for therapeutic or prophylactic use – 30.04
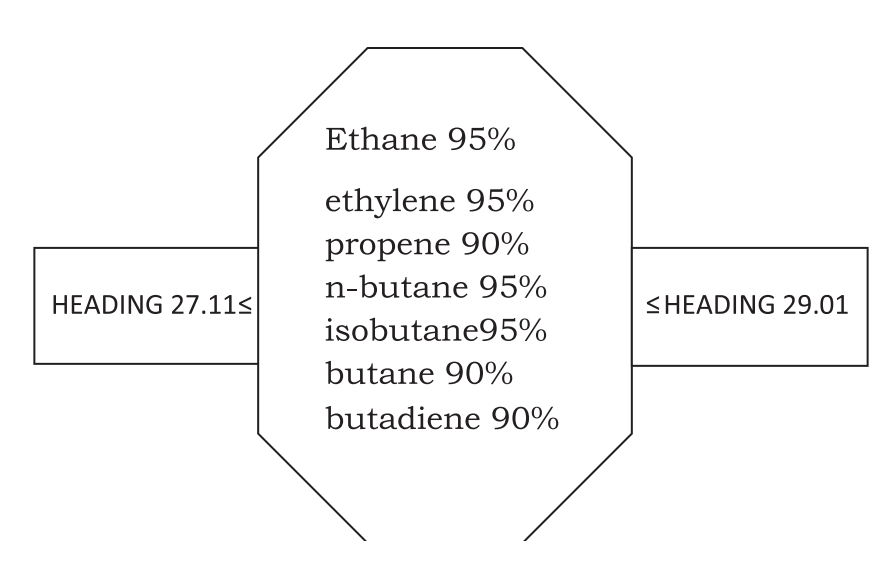
The above diagram shows classification of goods in heading 27.11 and heading 29.01 as
per the EN to heading 27.11 and EN to Heading 29.01.
For example, ethene with a level of purity less than 95% pure is classified in heading 27.11
not in heading 29.01.
heading 29.40 covers sugars chemically pure, others than sucrose, lactose, maltose,
glucose and fructose (Chapter 17). Sugar or Sucrose is classified in Chapter 17.

Preparation of Vitamins
Vitamins (Heading 29.36) are active agents, usually of complex chemical composition,
which are obtained from outside sources and are essential for the proper functioning of
human or other animal organisms (Explanatory Notes to heading 29.36).
Preparations based on vitamins are excluded from Chapter 29 and are classified in Chapters
21, 23, 30. Supplement feeds (used in animal feeding), containing antibiotics and vitamin
A, with dairy products are classified in Subheading 2309.90 (Preparations of a kind used
in animal feeding).
Vitamin and mineral supplements are classified in Chapter 21 (Miscellaneous edible
preparations), subheading 2106.90 (Other).
Multi vitamin preparations presented in soft gelatin capsules (main ingredients : ginseng
extract, vitamins, nicotinamide, calcium pantothenate) are also classified in subheading
2106.90.
Chapter 30: Pharmaceutical products
Pharmaceutical products
This Chapter is for pharmaceutical products classified in six headings,
- 30.01 Glands and other organs for organo-therapeutic uses
- 30.02 Blood and blood fractions, vaccines, modified immunological products
- 30.03 and 30.04 Medicaments
- 30.05 Bandages, gauze impregnated with pharmaceutical products
- 30.06 Pharmaceutical goods (specified in Note 4 to Chapter 30)
Medicaments
Medicaments are limited to products in medicine that contain, per dose, a sufficient
quantity of active substance with a curative or prophylactic effect against a particular
ailment or diseases, except certain special case.
The above guidance assists in determining a product to be classified as medicaments of
this Chapter.
Tablets, capsules and syrups which do cure or treat a particular ailment or disease are
not regarded medicaments. For example, aloe vera tablets put up for retail sale in plastic
containers, of which the tablets consist of 3% aloe vera powder used as a nutritional
supplement such product is considered a food supplement classified in heading 21.06.
Note 1(b) to Chapter 30 gives clarification on the classification of preparations such as
tablets having the nature of food supplements, chewing gum or patches intended to assist
smokers to stop smoking (heading 21.06 or 38.24).
While Note 1 excluded items from this chapter, it is also important to crosscheck with
Note 4 to Chapter 30 before considering classifying item in heading 30.06.
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover among others:
Foods or beverages (such as dietetic, diabetic or fortified foods, food supplements,
tonic beverages and mineral waters), other than nutritional preparations for intravenous
administration (Section IV); preparations, such as tablets, chewing gum or patches
(transderal system), intended to assist smokers to stop smoking (heading 21.06 or 38.24),
plasters specially calcined or finely ground for use in dentistry (heading 25.20). (Note 1
to Chapter 30).
Chapter 31: Fertilizers
Fertilizers
This Chapter covers fertilizers natural fertilizers either from vegetables or animals in
heading 31.01, chemically produced fertilizers in headings 31.02 to 31.05.
Special features
Packing of fertilizer either in bags of up to 10kgs or in tablet forms is a unique feature of
heading 31.05. Therefore, all types of fertilizer are classified in this heading provided they
are packed in this design.
The last category to fall in this heading are other fertilizers which are not of any of the
three fertilizing elements neither nitrogenous (N), phosphorus (P), nor potassium (K).
Headings 31.02 to 31.04 cover fertilizers having only one type of fertilizing element.
Chapter 32: Tanning or dyeing extracts
Tanning or dyeing extracts; tannins and their derivatives; dyes,
pigments and other colouring matter; paints and varnishes; putty and other
mastics; inks
This Chapter covers preparations used in the tanning and bating of hides and skins, coloring
matter of vegetable, animal or mineral origin and synthetic organic coloring matter and
most preparations of the coloring matters, for example, paints, inks, ceramic colors, among
others. It also includes preparations such as varnishes, driers, and putty.
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover :
Separate chemically defined elements or compounds (except those of heading 32.03 or
32.04, inorganic products of a kind used as luminophores (heading 32.06), glass obtained
from fused quartz or other fused silica in the forms provided for in heading 32.07, and
also, dyes and other coloring matter put up in forms or packing for retail sale, of heading
32.12); tannates or other tannin derivatives of products of headings 29.36 to 29.39, 29.41
or 35.01 to 35.04; or Mastics of asphalt or other bituminous mastics (heading 27.15).
Chapter 33: Essential oils and resinoids
Essential oils and resinoids; perfumery, cosmetic or toilet preparations
This chapter covers essential oils and extracted oleoresins, concretes (solid or semi-solid
due to the presence of plant waxes), mixtures provided they are a kind used as raw materials
in (perfumery, food or drink industries), perfumes, and toilet waters.
Special features
The expression “odoriferous substances” in heading 33.02 refers only to the substances of
heading 33.01, to odoriferous constituents isolated from those substances or to synthetic
aromatics. Headings 33.03 to 33.07 apply, inter alia, to products, whether or not mixed
(other than aqueous distillates and aqueous solutions of essential oils), suitable for use
as goods of these headings and put up in packings of a kind sold by retail for such use.
The expression “perfumery, cosmetic or toilet preparations” in heading 33.07 applies,
inter alia, to the following products: scented sachets; odoriferous preparations which
operate by burning; perfumed papers and papers impregnated or coated with cosmetics;
contact lens or artificial eye solutions; wadding, felt and nonwovens, impregnated, coated
or covered with perfume or cosmetics; animal toilet preparations.
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover natural oleoresins or vegetable extracts of heading 13.01 or
13.02; Soap or other products of heading 34.01; gum, wood or sulfate turpentine or other
products of heading 38.05.
Chapter 34: Soap, organic surface-active agents,
Soap, organic surface-active agents, washing preparations,
lubricating preparations, artificial waxes, prepared waxes, polishing or
scouring preparations, candles and similar articles, modeling pastes, “dental
waxes” and dental preparations with a basis of plaster
This Chapter covers products mainly obtained by the industrial treatment of fats, oils or
waxes. It also includes certain artificial products for example surface-active agents, surface
active preparations and artificial waxes. The Chapter doesn’t cover separate chemically
defined compounds, or natural products not mixed or prepared.
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover edible mixtures or preparations of animal or vegetable fats
or oils of a kind used as mold release preparations (heading 15.17); separate chemically
defined compounds; or shampoos, dentifrices, shaving creams, and foams, or bath
preparations, containing soap or other organic surface-active agents (heading 33.05, 33.06
or 33.07).
Chapter 35: Albuminoidal substances; modified starches; glues; enzymes
Albuminoidal substances; modified starches; glues; enzymes
This Chapter covers casein, caseinates and casein derivatives; casein glues, albumins,
albuminates, gelatin, gelatin derivatives, pop tones, dextrins.
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover yeast (heading 21.02), hardened protein (heading 39.13)
blood fraction, medicament, among others.
Chapter 36: Explosives; pyrotechnic products
Explosives; pyrotechnic products; matches; pyrophoric alloys;
certain combustible preparations
This Chapter covers propellent powders and prepared explosives, viz, mixtures
characterized by the fact that they contain the oxygen necessary for combustion and that
in combustion they produce a large volume of gas at a high temperature, articles prepared
from explosives, pyrophoric, inflammable or combustible products for producing light,
sound, smoke, flame or sparks.
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover separate chemically defined compounds other than those
described in Note 2(a) or (b) to Chapter 36.
Chapter 37: Photographic or cinematographic goods
Photographic or cinematographic goods
This Chapter covers photographic plates, film, paper, paperboard and textiles of Chapter
37 are those with one or more layers of any emulsion sensitive to light or other forms of
radiation. In this Chapter the word “photographic” relates to the process by which visible
images are formed, directly or indirectly, by the action of light or other forms of radiation
on photosensitive surfaces.
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover waste or scrap of Chapter 38.
Chapter 38: Miscellaneous chemical products
Miscellaneous chemical products
This Chapter covers miscellaneous chemical products not covered somewhere else in
the Nomenclature. It is sometimes known as basket Chapter for chemicals not covered
somewhere else in the Nomenclature. It also covers separate chemical defined compounds
put up in packages for retail sale not covered elsewhere in other Chapters of the nomenclature.
For example sulphur-treated bands, wicks and candles, and fly paper insect-side of 38.08
which otherwise are classified as sulphur chemicals of Chapter 28.
The Chapter also covers wastes as provided by Notes 4, 5, and 6 to the Chapter 38 for
municipal waste, sewage sludge, and other waste respectively. However, wastes containing
mainly petroleum oil remain classified in Chapter 27 as per note 6 to Chapter 38.
Biodiesel is also classified in this Chapter if it contains less than 70% of petroleum oils
(38.26. Biodiesel is defined in note 7 to Chapter 38.
Classification of pesticides is based on Note 2 to Section VI which reads;
Subject to Note 1 above, goods classified in heading 30.04, 30.05, 30.06, 32.12, 33.03,
33.04, 33.05, 33.06, 33.07, 35.06, 37.07 or 38.08 by reason of being put up in measured
doses or for retail sale are to be classified in those headings and in no other heading of
the Nomenclature.
38.08 – Insecticides, rodenticides, fungicides, herbicides, anti-sprouting products and
plant-growth regulators, disinfectants and similar products, put up in forms or packings
for retail sale or as preparations or articles (for example, sulphur-treated bands, wicks and
candles, and fly papers).
The nature of packaging determines classification. When Separate chemically defined
compounds for example DDT are presented in form or packaging for retail sale, they are
classified in heading 38.08, subheading 3808.91 However, when they are presented in
bulk, they are classified in Chapter 29, subheading 2903.92.
Relationship with other Chapters
This Chapter does not cover;
(a) Separate chemically defined elements or compounds with the exception of the following;
(1) Artificial graphite (heading 38.01);
(2) Insecticides, rodentcides, fungicides, herbicides, anti-sprouting products and
plant-growth regulators, disinfectants and similar products, put up as described
in heading 38.08;
(3) Products put up as charges for fire-extinguishers or put up in fire-extinguishing
grenades (heading 38.13);
(4) Certified reference materials specified in Note 2 to Chapter 38;
(5) Products specified in Note 3 (a) or 3 (c) to Chapter 38.
(b) Mixtures of chemicals with foodstuffs or other substances with nutritive value, of a
kind used in the preparation of human foodstuffs (generally heading 21.06);
(c ) Ash and residues ( including sludges, other than sewage sludge), containing metals,
arsenic or their mixtures and meeting the requirements of Note 3(a) or 3(b) to Chapter
26 (heading 26.20);
(d) Medicaments (heading 30.03 or 30.04); or
(e) Spent catalysts of a kind used for the extraction of base metals or for the manufacture
of chemical compounds of base metals (heading 26.20), spent catalysts of a kind used
principally for the recovery of precious metal (heading 71.12) or catalysts consisting
of metals or metal alloys in the form of, for example, finely divided powder or woven
gauze (Section XIV or XV).
Special features
Note 3 to chapter 38 read that heading 38.24 includes the following goods which are
not to be classified in any other heading of the Nomenclature :
(a) Cultured crystals (other than optical elements) weighing not less than 2.5g
each, of magnesium oxide or of the halides of the alkali or alkaline-earth
metals;
(b) Fusel oil; Dippel’s oil;
(c) Ink removers put up in packings for retail sale;
(d) Stencil correctors, other correcting fluids, and correction tapes (other than
those of heading 96.12), put up in packing for retail sale; and
(e) Ceramic firing testers, fusible (for example, Seger cones).
Note 7 to Chapter 38 reads, for the purpose of heading 38.26, the term ‘biodiesel’ means
mono-alkyls esters of fatty acids of a kind used as a fuel, derived from animal or vegetable
fats and oils whether or not used.
