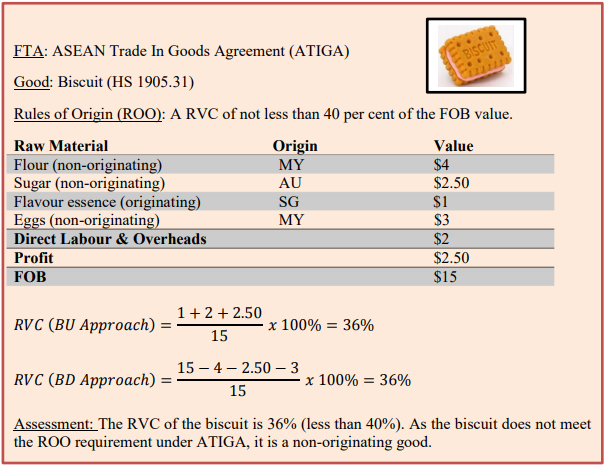
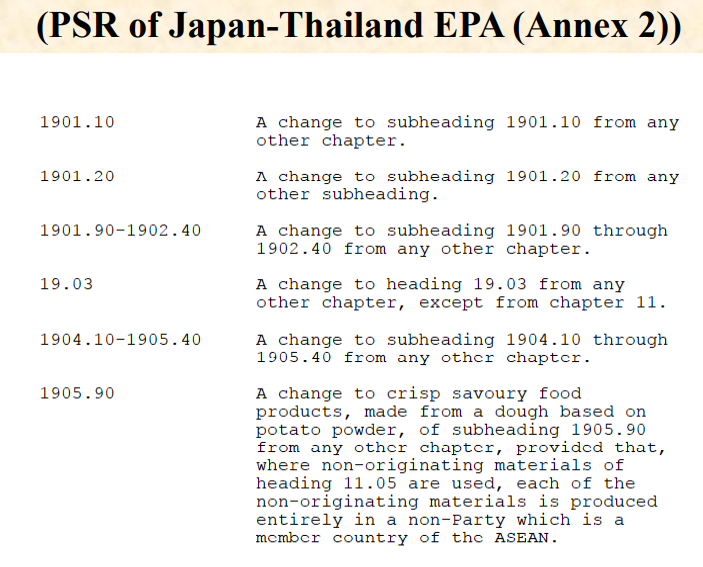
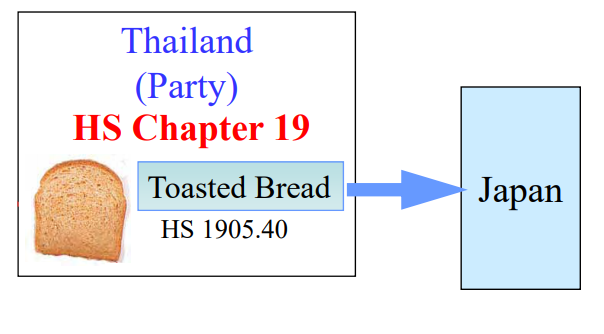
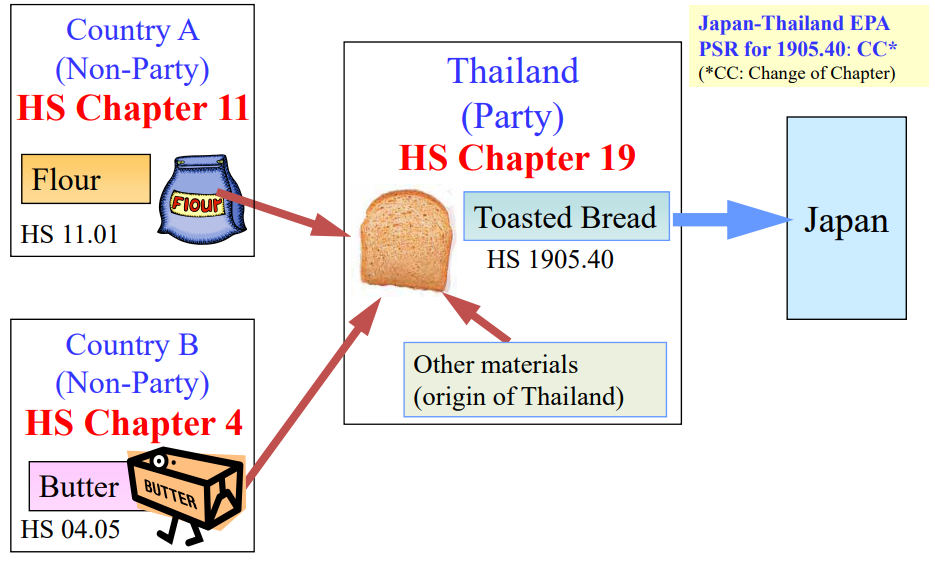
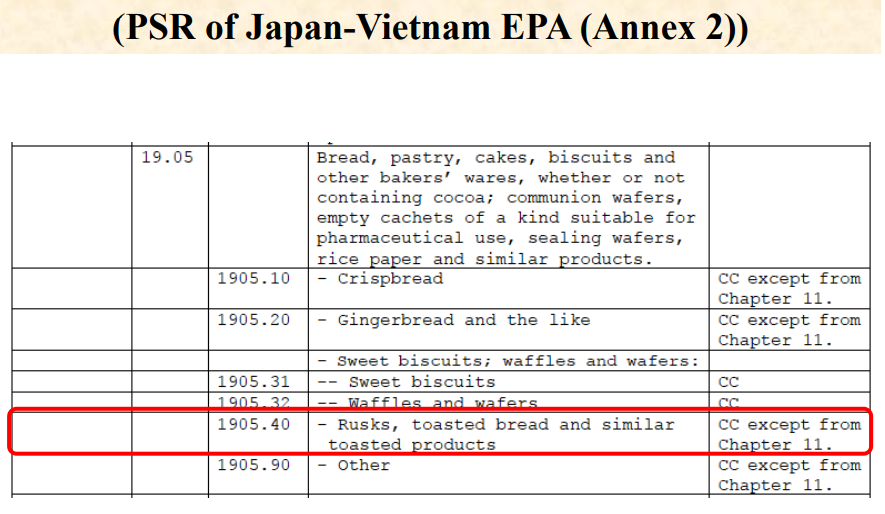
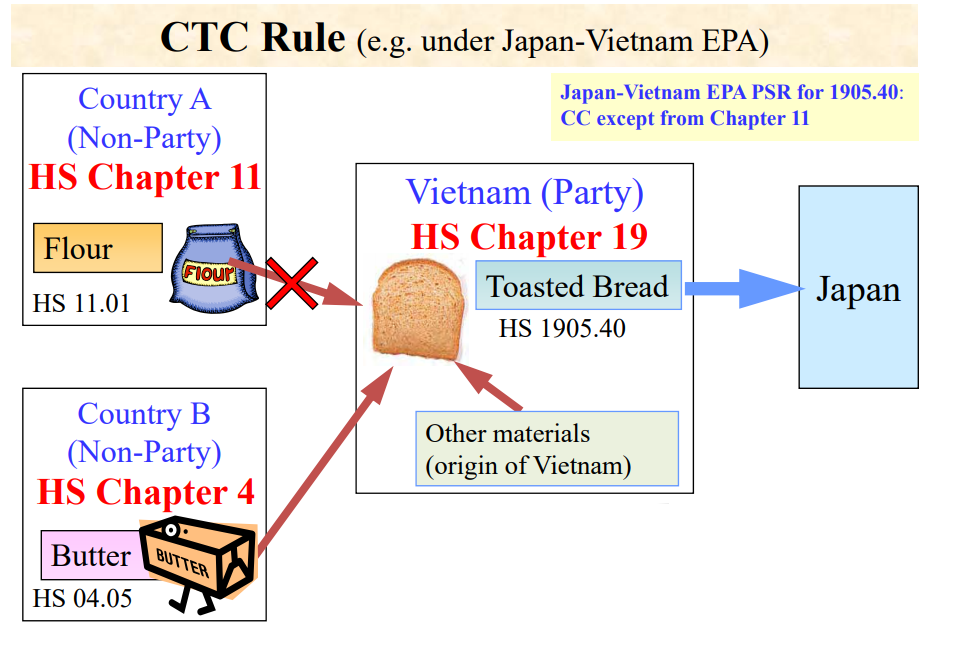
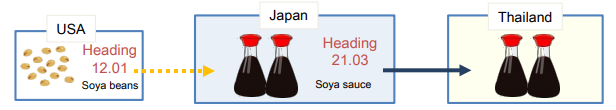
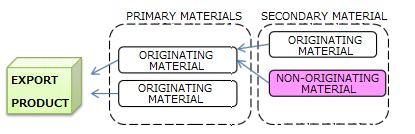
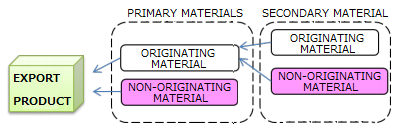
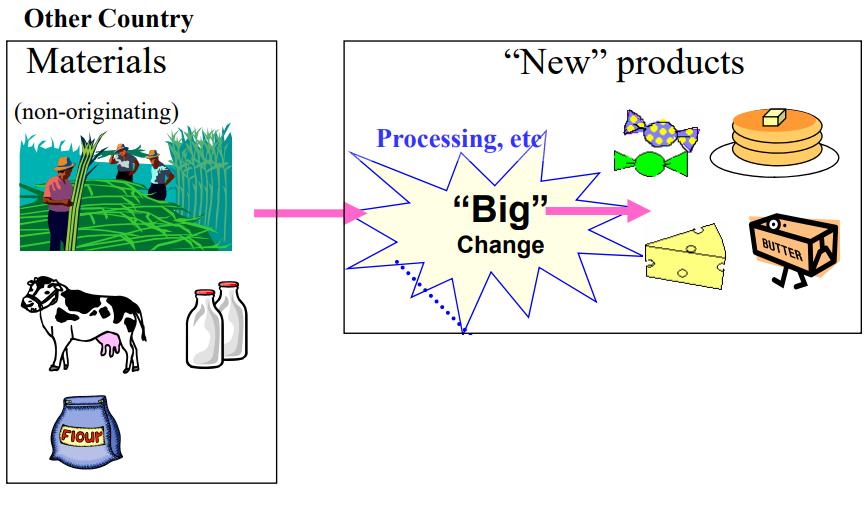
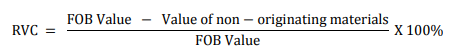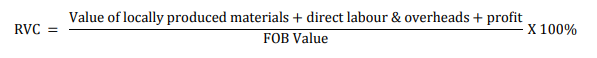Goods are considered as originating if the goods undergo specific manufacturing or processing such as
chemical reaction, distillation, purification, etc. in the territory of a party/country.
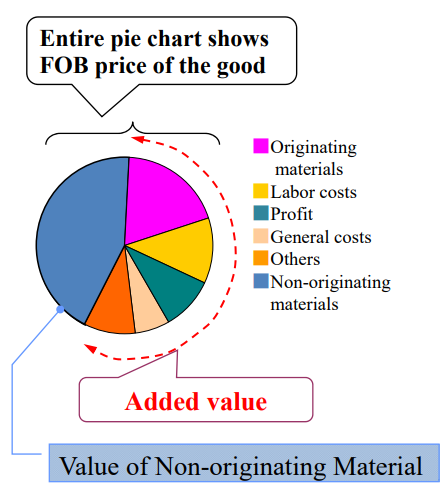
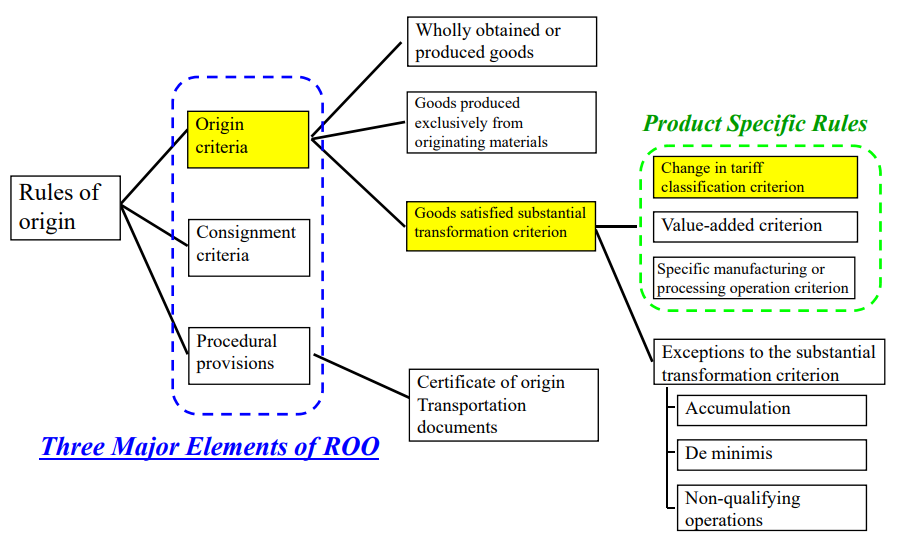
 Retrieved from: Outline of Rules of Origin for EPA in Japan
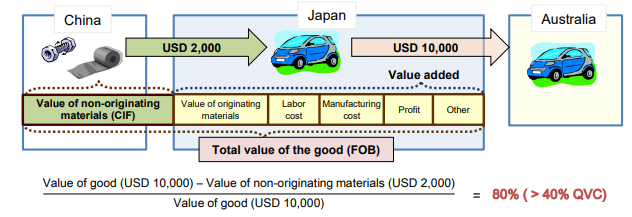
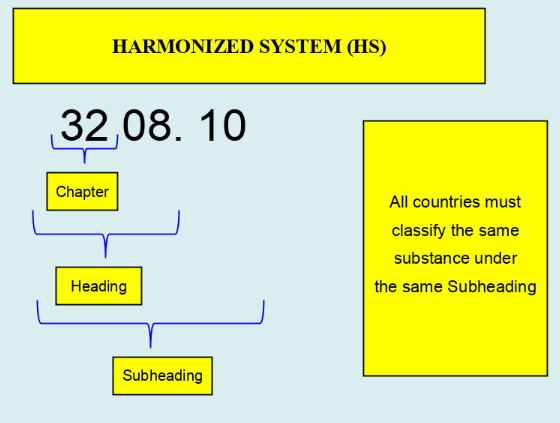
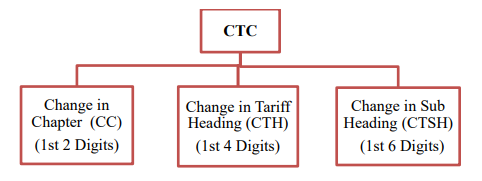
Retrieved from: Outline of Rules of Origin for EPA in Japan
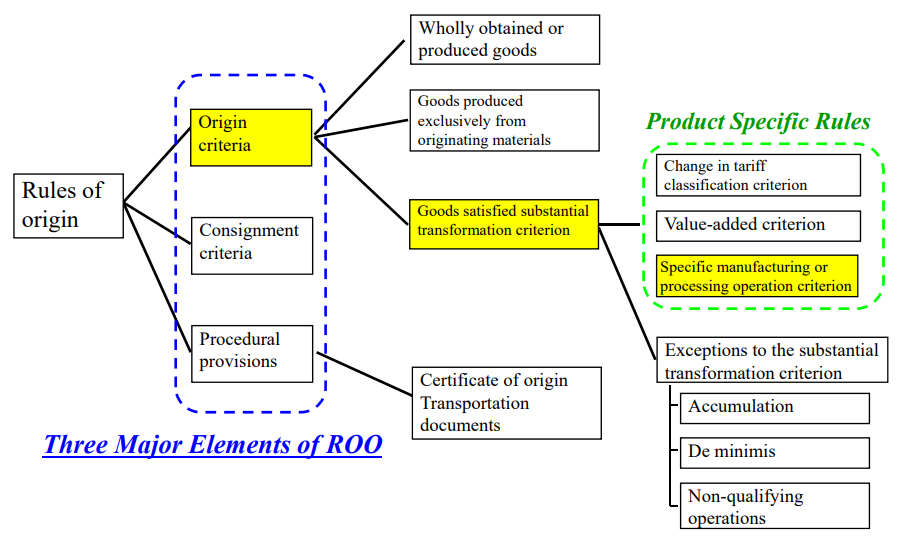
Definition of Specific manufacturing
Regardless of any change in its classification or the extent of value added,
a product is considered to be substantially transformed when it has undergone
a specific manufacturing or processing operation which is described in the
product specific list rules.
A good is considered as originating when the manufacturing operation described
for the respective commodity was carried out.
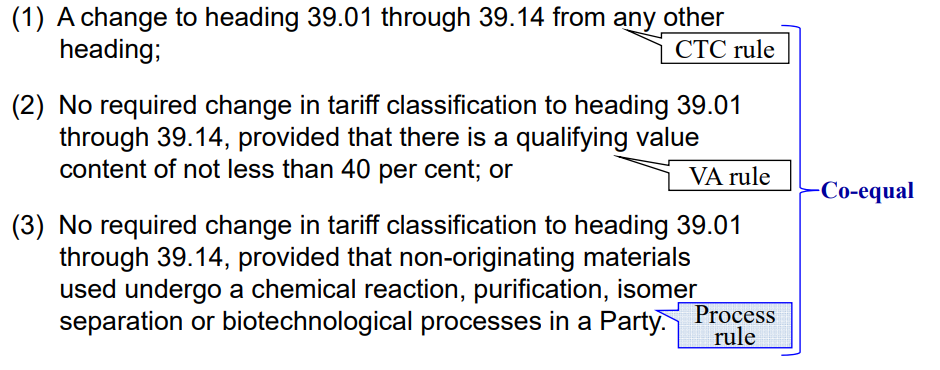
Example
In the case of “Chemical Products”
PSR for glycerol of subheading 2905.45 under Japan-Australia EPA:
“the good has undergone a chemical reaction in the area of a party.
Chemical reaction is defined as a process which results in a molecule with a new structure.”
Retrieved from: Outline of Rules of Origin for EPA in Japan
In the case of “Marble Products”
PSR for Marble of heading 25.15 under PAN-EURO-MED origin system:
Cutting, by sawing or otherwise, of marble (even if already
sawn) of a thickness exceeding 25 cm

Retrieved from:Comparative Study on Preferential Rules of Origin
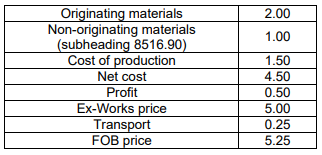
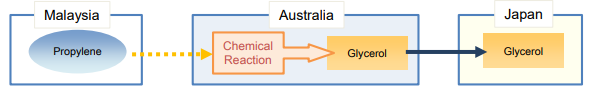
In the case of “Polypropylene paste “
PSR for Polypropylene paste of subheading 3902.10 under
Japan-Singapore Economic Partnership Agreement(JSEPA):
No required change in tariff
classification to heading 39.01 through
39.26, provided that non-originating
materials used undergo a chemical
reaction, purification, isomer
separation or biotechnological
processes in a Party.

Assessment: Polypropylene paste is produced from propylene by a process known as
metallocene catalysis polymerization, which is a form of chemical reaction. As,
Polypropylene meets the ROO under JSEPA, it is an originating good.
Retrieved from:Handbook on Rules of Origin for Preferential Certificates of Origin
The methodology of specific manufacturing/processing operations is widely used in the
PAN-EURO-MED origin system. In the textile and apparel sector, this methodology is
commonly used in the ATIGA, the NAFTA, the PAN-EURO-MED and the TPP origin systems.
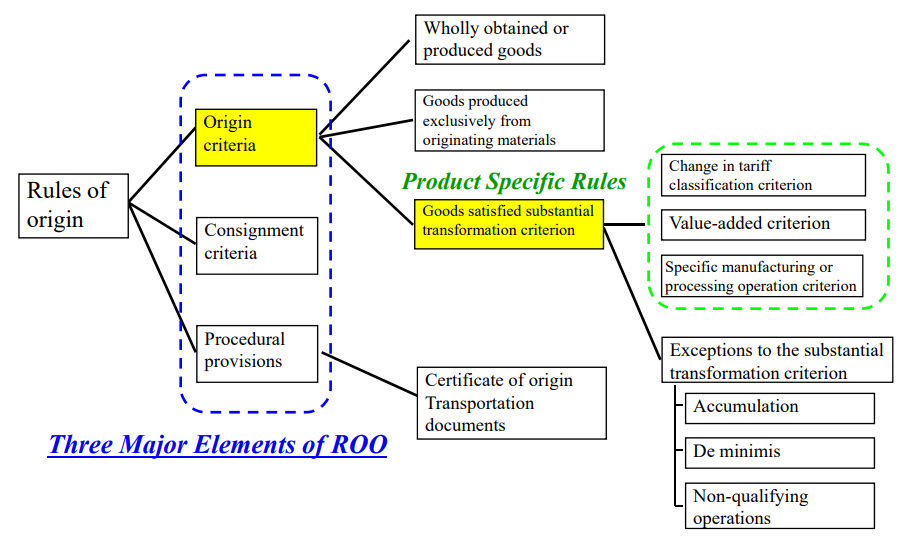
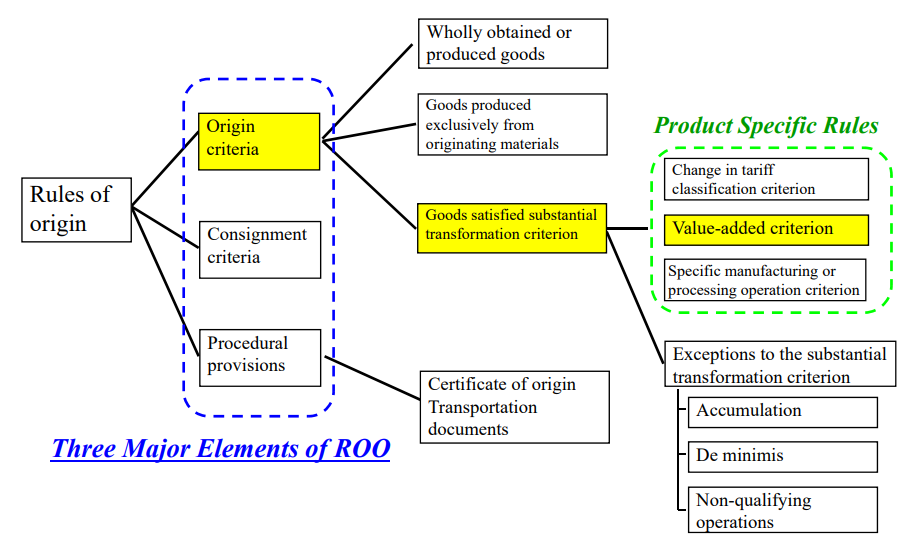
The Specific Manufacturing or Processing Operations criterion has specific features as follows:
Features of the Specific Manufacturing or Processing Operations Criterion:
■Specific manufacturing operations are objective and unambiguous;
■Rules can be drafted in an easily understandable manner;
■Frequent modifications may be needed to catch up with technical developments;
■To be precise, longer and more detailed texts are needed;
■The rules vary from product to product;
■Frequent need of new rules for new products.
 Retrieved from:
Retrieved from: