Regardless of changes in its tariff classification, a product is considered as
originating when the value of the product is increased up to a specified level
expressed by an ad valorem percentage.
The rules based on a value-added/ad-valorem criterion may be described
primarily in two distinct ways:
a maximum allowance for non-originating materials
maximum third country content allowance, meaning that a final product can be
considered as an originating product provided that the foreign inputs do not
exceed a certain threshold;
Example 1
A drilling machine of heading 84.59 is manufactured from the following materials:

| Parts & Costs | Origin | Value |
| case with origin from a free trade partner country | Originating | 100 |
| electronic control panel, from country outside the free trade area |
Non-Originating | 250 |
| electric motor, from country outside the free trade area | Non-Originating | 100 |
| other parts of undetermined origin | Non-Originating | 50 |
| labour costs and manufacturer’s profit margin | 500 | |
| Selling price of the final drilling machine(Ex-works) | 1000 |
Product-specific rule (European model) for headings 84.56 to 84.66 is
Manufacture in which the value of all the non-originating materials used does
not exceed 40 % of the ex-works price of the product.
Thus, the value of the non-originating materials incorporated in the drill
(electronic control panels, motor and other parts = value 400)
(N.B. input with undetermined origin counts as non-originating input) does not
exceed 40 % of its ex-works price,
i.e., the percentage required for substantial transformation;
the drill therefore qualifies as the originating product.
a minimum requirement of domestic content
a minimum requirement of domestic content, meaning that a final product can be
considered as an originating product provided that the domestic inputs exceed a
certain threshold;
Example 2
An electric hair curling iron (subheading 8516.32)
| Parts & Costs | Cost | Origin | Value |
| Non-originating materials(8516.90) | Net-cost | Non-Originating | 1.2 |
| Cost of production | Net-cost | 2.45 | |
| Profit | Cost | 0.5 | |
| Transport | Cost | 0.25 | |
| FOB Price | 4.4 |
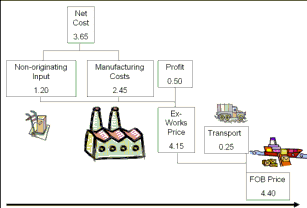
An electric hair curling iron (subheading 8516.32) is made in Mexico from
Japanese hair curler parts (8516.90). Selling price value 4.40; the value of
the non-originating hair curler parts is 1.20.
Product-specific rule (European model) for headings 8516.32 is
A change to subheading 8516.32 from subheading 8516.80 or any other
heading; or
A change to subheading 8516.32 from subheading 8516.90,
whether or not there is also a change from subheading 8516.80 or
any other heading,
provided there is a regional value content of not less than:
a. 60 percent where the transaction value method is used, or
b. 50 percent where the net cost method is used.
The first tariff shift rule requirement(a) is not met, meaning that the second rule(b)
combines a tariff shift rule with a regional value content requirement.
In our example, both the transaction value method and the net cost method are fulfilled:

Note1: In this situation “Net cost” is the total sum of a “Non-originating materials” and
“Cost of production”
Note2:Net cost represents all of the costs incurred by the producer minus expenses for
sales promotion (including marketing and after-sales service), royalties, shipping
and packing costs and non-allowable interest costs.
