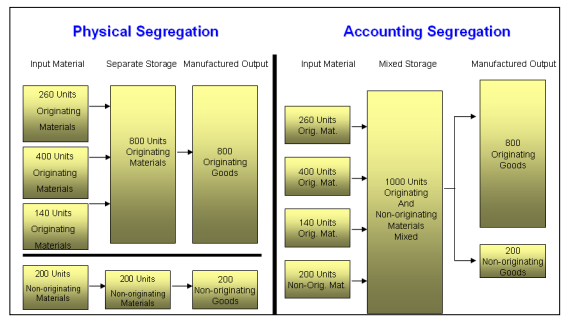
If manufacturers use originating and non-originating materials – even if
these are identical and interchangeable – under normal circumstances,
they are required to stock those materials separately to allow tracing back of
the different origins of materials used in the production of goods.
This ensures that only originating input is used for the manufacturing of
originating goods intended for export under preferences.
The requirement to stock originating and non-originating input material separately
may represent a huge financial burden for the manufactures.
Therefore, provisions on accounting segregation/fungible goods and materials offer
the possibility to use accounting methods to determine the different origins of input
materials or goods which are identical and interchangeable, without any obligation to
physically segregate stocks of non-originating and originating materials or goods.
Retrieved from:WCO ORIGIN COMPENDIUM
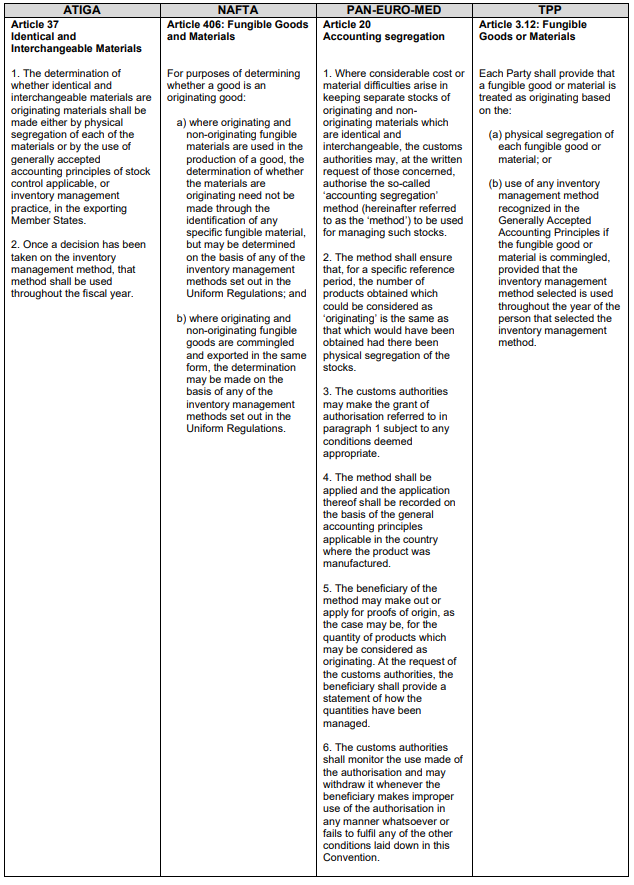
The method is called “Identical and Interchangeable Materials” in the ATIGA context,
“Accounting Segregation” in the PAN-EURO-MED origin system and “Fungible Goods
and Materials” in the NAFTA and TPP context.
In all four origin legislations the physical mix of non-originating and originating input
materials are limited to ‘fungible’ commodities,
i.e. commodities which are identical and interchangeable.
In the European and the ASEAN origin legislations the application of this method is
limited to materials and not allowed for finished products whereas in the NAFTA and
TPP contexts there are no such distinctions.
According to the NAFTA legislation the use of accounting methods to distinguish
originating and non-originating commodities in the manufacture of originating goods
is permitted. The same applies to the TPP Agreement and it states that the inventory
management selected should be applied throughout the year, however in the
PAN-EURO-MED origin system there is the requirement for a specific authorization by
the customs authorities for the use of such a method and the use of the method is
limited to such cases where keeping separate stocks of originating and non-originating
materials would result in considerable costs or material difficulties.
Such preconditions are not required in the ATIGA, the NAFTA and the TPP contexts.
Comparison of “Accounting Segregation/Fungible Goods and Materials”
Retrieved from:Comparative Study on Preferential Rules of Origin
Related Study Module on “Accounting Segregation/Fungible Goods”
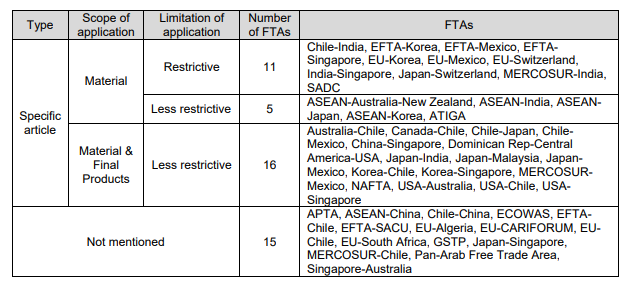
This study module aims to compare and analyse the features of Rules of Origin (ROO)
provisions of the selected 47 Free Trade Agreements (FTA). This module intends to sort out
the types of various topics of ROO provisions.
The following table is the comparison of accounting segregation / fungible goods in the
selected FTAs.
Retrieved from:Comparative Study on Preferential Rules of Origin
