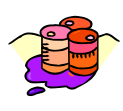
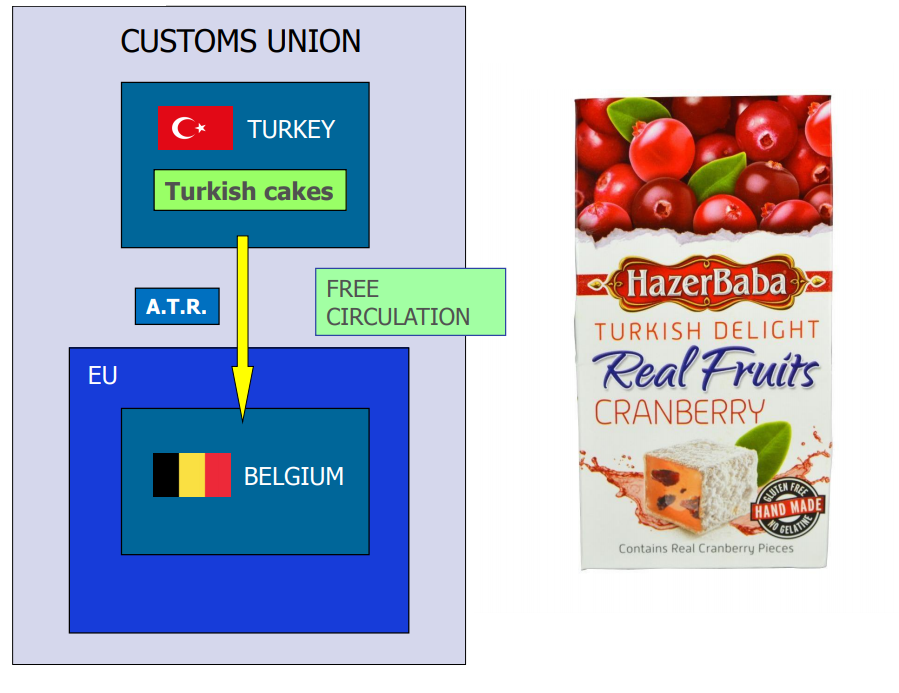
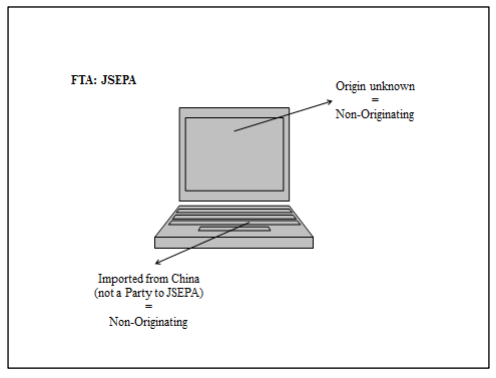
Goods that are produced using non-originating materials will have to undergo
substantial transformation in a country for the good to be qualified as originating.
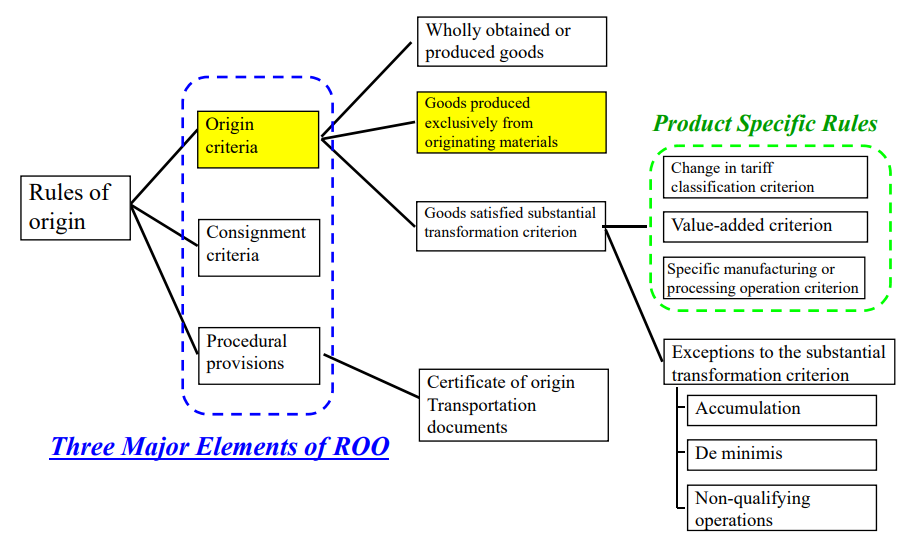
The methods “product-specific rules (PSR)” used to measure the transformation are:
a) “Change in tariff classification criterion(CTC)”,
b) “Value-added criterion (VA,RVC)”, or
c) “Specific manufacturing or processing operation criterion (SP)”.
These 3 methods can be used in combination or standalone, depending on the origin criteria(on) for the good in a Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
The origin of these goods would be dependent on the country where the last substantial transformation is performed.
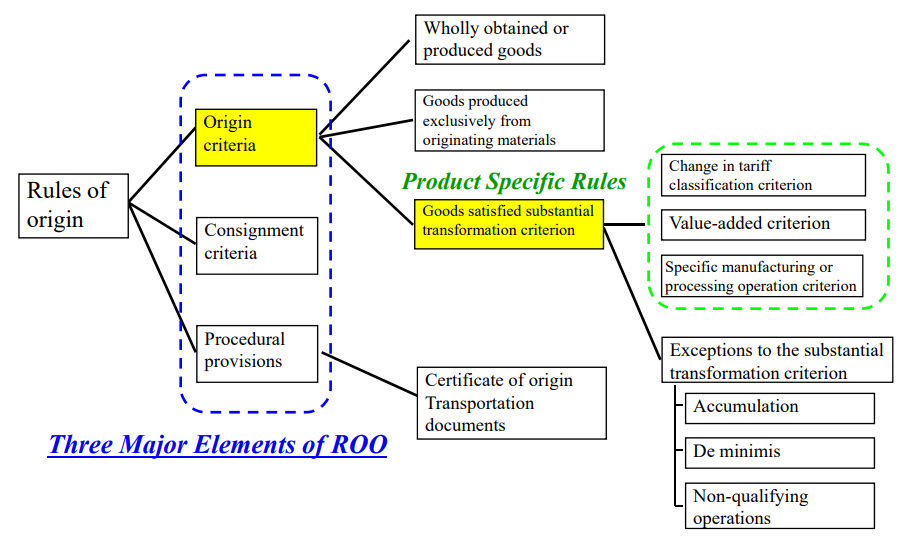
Retrieved from: Outline of Rules of Origin for EPA in Japan
PSR is stipulated in an annex to each FTA
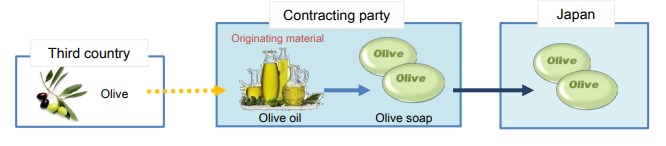
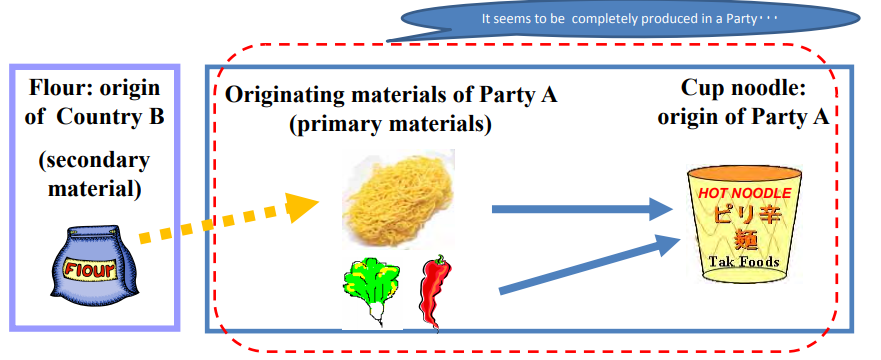
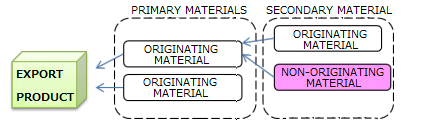
Even if the materials from third countries (non-originating materials) are used in the
production, goods are considered as originating when the goods satisfy the
requirement set out in the product-specific rules(PSR).
PSR is generally provided as an annex to each FTA.
Here is an example of Product-Specific Rules (PSR) stipulated in an annex to
Japan-Thailand EPA

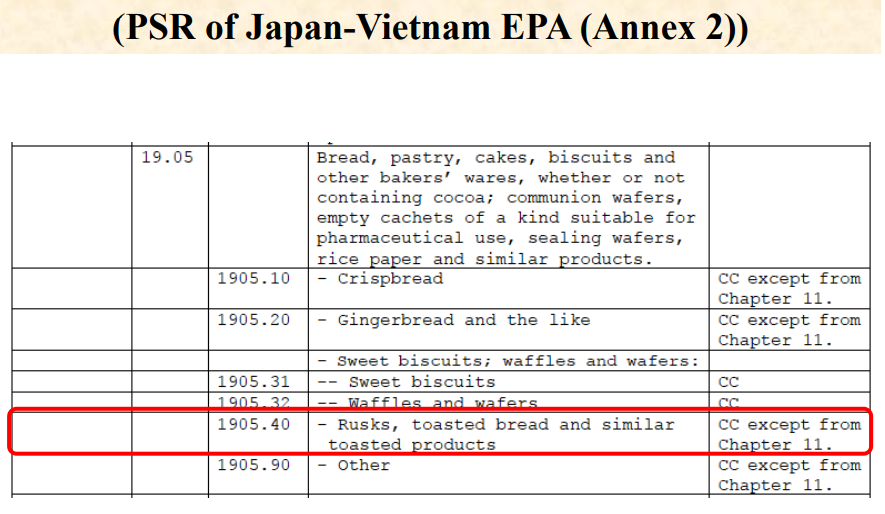
Here is an example of Product-Specific Rules (PSR) stipulated in an annex to
Japan-Vietnam EPA
Require “Big change” to be considered as an originating good
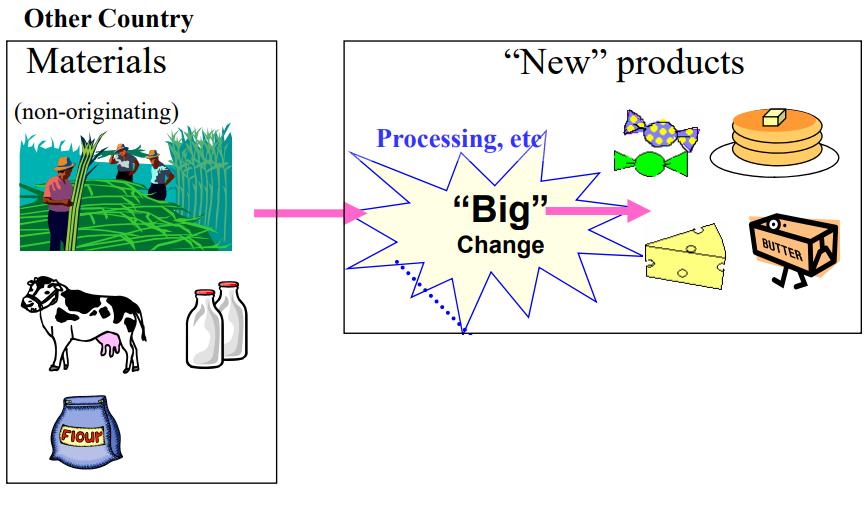
Retrieved from: Outline of Rules of Origin for EPA in Japan
This “Big change” is named as “substantial transformation” and a Party in which such a big change happened is considered as an origin of the Party.
Goods underwent big change are named as “Goods satisfied substantial transformation criterion”.
3 types of Substantial Transformation (Big Change)
(1) Change-in-tariff-classification Criterion (CTC rule)
When the HS code of a good differs from all HS codes of non-originating materials,
the good is qualified as an originating good.
For more details see What is “Change in tariff classification criterion(CTC)”
(2) Value-added criterion (VA rule)
When the value added to a good through its production in a Party satisfies some value content
the good is qualified as a Party satisfies some value content, the good is qualified as an
originating good.
For more details see What is “Value-added criterion”
(3) Specific manufacturing or processing operation (SP rule)
When specific manufacturing or processing operation is applied to all non-originating materials,
the good is qualified as an originating good.
For more details see What is “Specific manufacturing or processing operation criterion (SP)”
Example of PSR
PSR for subheading 3904.10(Polyvinyl Chloride) under Japan-Thailand EPA
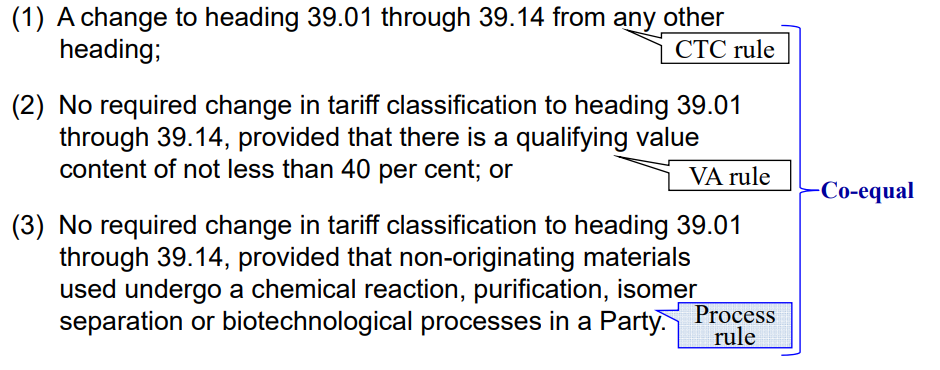
PSR for a good classified in subheading 3904.10 is composed of 3 criteria and
there is no priority order among these criteria (Co-equal rule) If one of these
criteria is met it satisfies PSR.