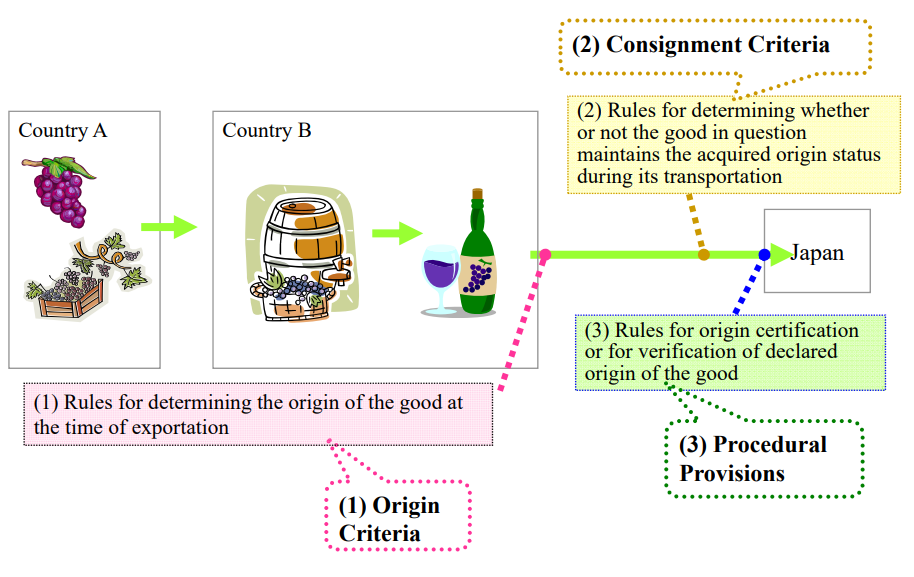
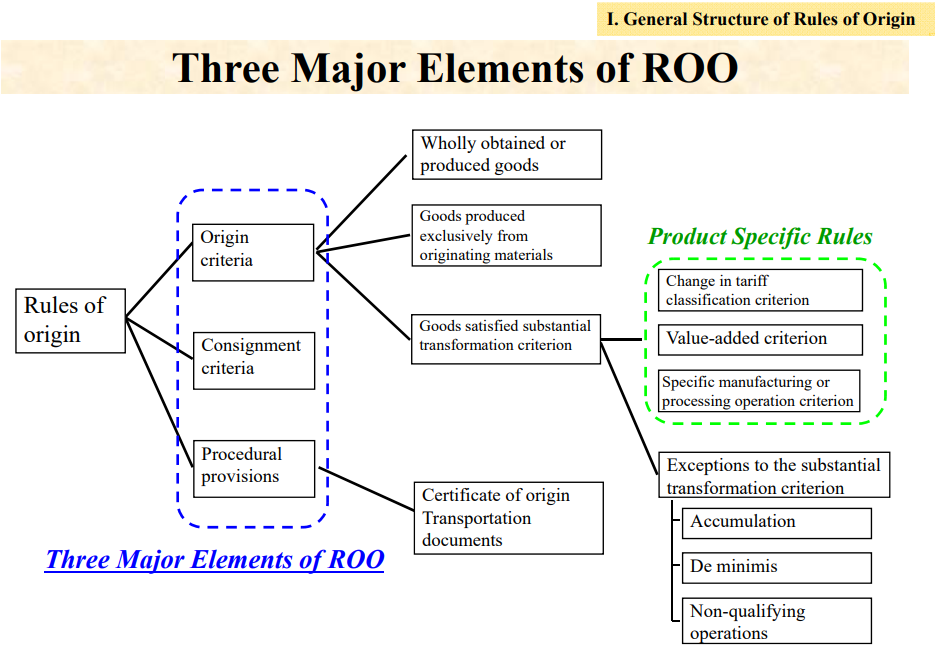
Rules of origin generally consists of origin criteria and origin procedures.
Origin criteria stipulate conditions or requirement for a good to be
considered as ‘originating’.
Origin procedures provide for the course of action to be followed when
applying the preferential Customs Duty rates.
Three major parts of Origin Criteria
In general, originating goods are either:
“Wholly obtained goods(WO)”,
“Goods produced exclusively from originating materials(PE)”, or
“Goods satisfying the product-specific rules (PSR)”.
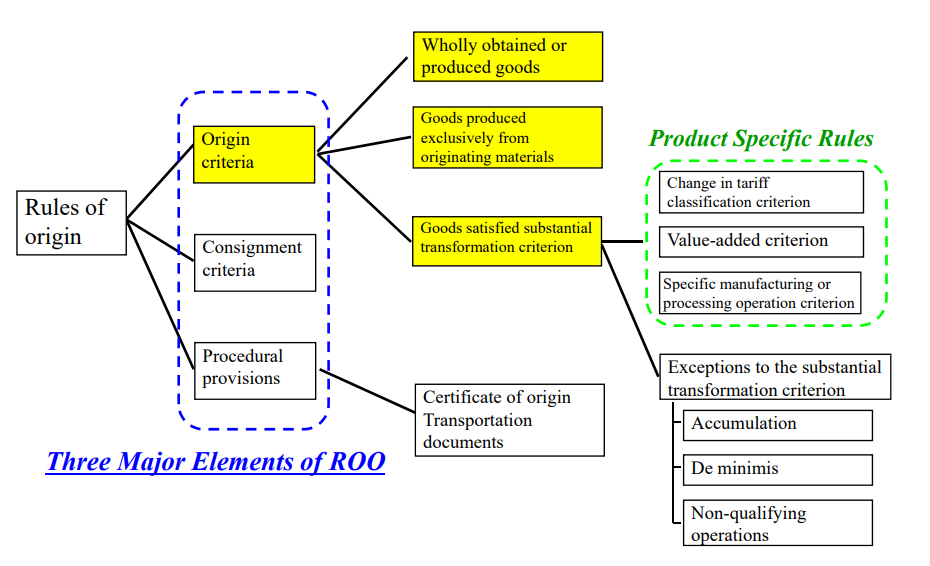
Please note that the rules of origin of each FTA reflect the result of negotiations
with the partner countries, thus there are slight differences from one agreement
to another.
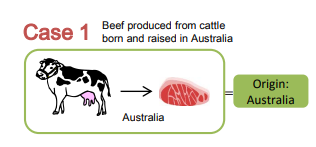
Wholly obtained goods(WO)
Wholly obtained goods are the goods whose production is completed in one country
(a)live animals born and raised in the Party (Livestock, etc.)
(b)animals obtained by hunting, trapping, fishing,
gathering or capturing in the Party (Captured wild animals, etc.)

(c) goods obtained from live animals in the Party (Milk, egg, etc.)

(d)plants and plant products harvested, picked or gathered in the Party
(Cut flowers, etc.)

(e)minerals and other naturally occurring substances, not included
in subparagraphs (a) through (d) above, extracted or taken in the Party
(f) goods of sea-fishing and other goods taken by vessels of the Party
from the sea outside the territorial seas of the Partied

(l) goods obtained or produced in the Party exclusively from the goods
are referred to in subparagraphs (a) through (f) above
(Meat produced from slaughtered cattle, etc.)

Retrieved from: Outline of Rules of Origin for EPA in Japan
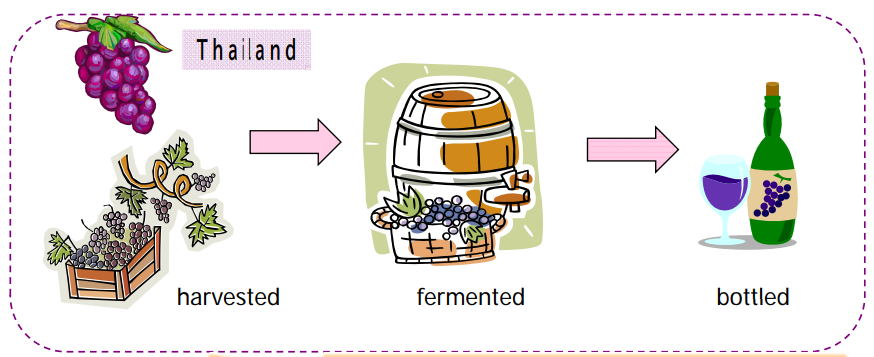
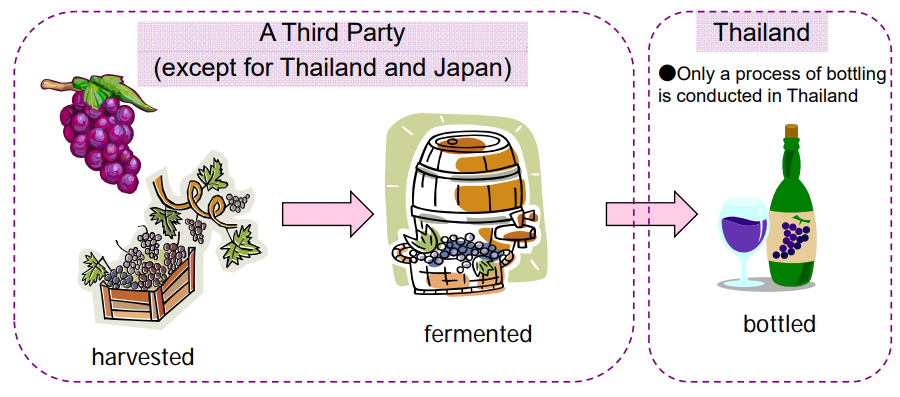
Images of “Wholly obtained goods”
Those are a typical example of “Wholly obtained goods”
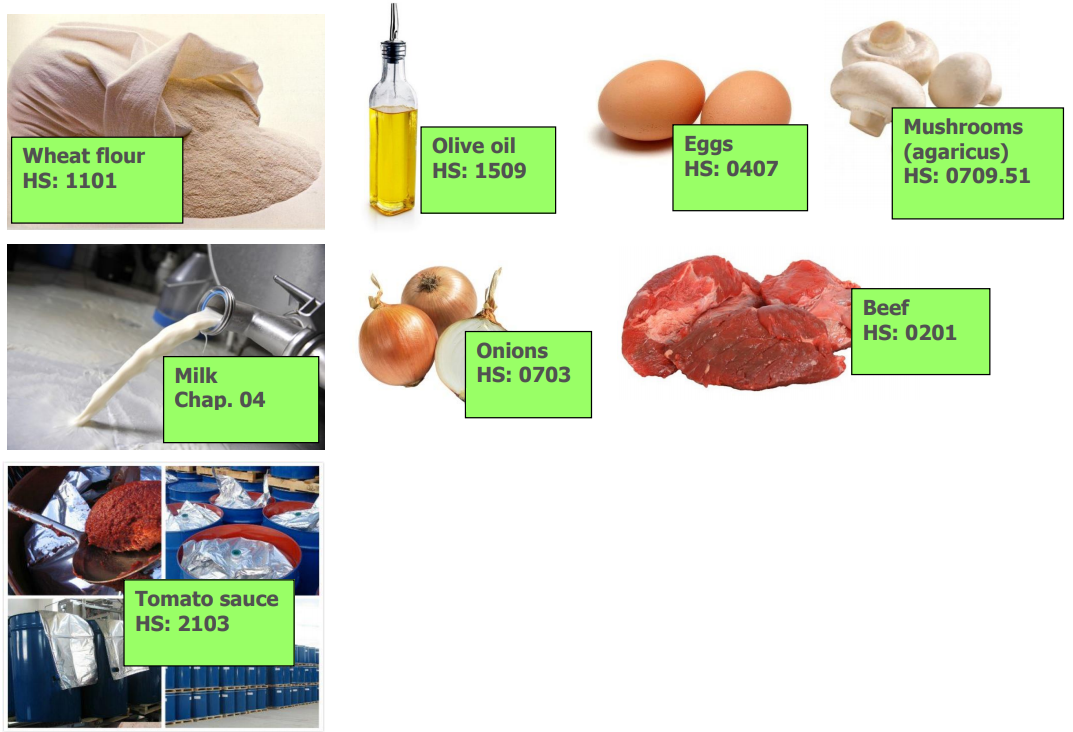
In the case below all components used are originating in Turkey.
Therefore the product is wholly obtained in Turkey.
Retrieved from:CHAMBRE DE COMMERCE ET D’INDUSTRIE DU LUXEMBOURG BELGE
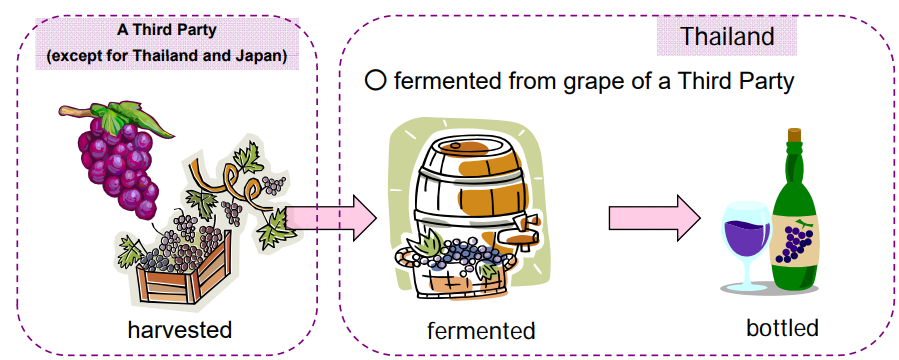
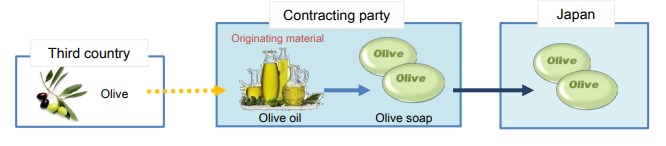
Goods produced exclusively from originating materials(PE)
Goods produced exclusively from originating materials are the goods produced
using originating materials only.
Because all the materials used in the production are originating materials,
the production is seemingly completed in one country.
However, there is a case where materials from a third country
(i.e. non-originating materials) are used in the production of the originating materials.
Goods satisfying the product-specific rules (PSR)
Goods that are produced using non-originating materials will have to undergo
substantial transformation in a country for the good to be qualified as originating.
Even if the materials from third countries (non-originating materials) are used
in the production, goods are considered as originating when the goods satisfy
the requirement set out in the Rroduct-Specific Rules (PSR).
PSR is generally provided as an annex to each FTA.
The methods used to measure the substantial transformation are:
1.“Change in Tariff Classification(CTC)”,
2.“Qualifying/Regional Value Content(QVC or RVC)”,
3.“Specific manufacturing or Processing(SP)”, or a combination of these.
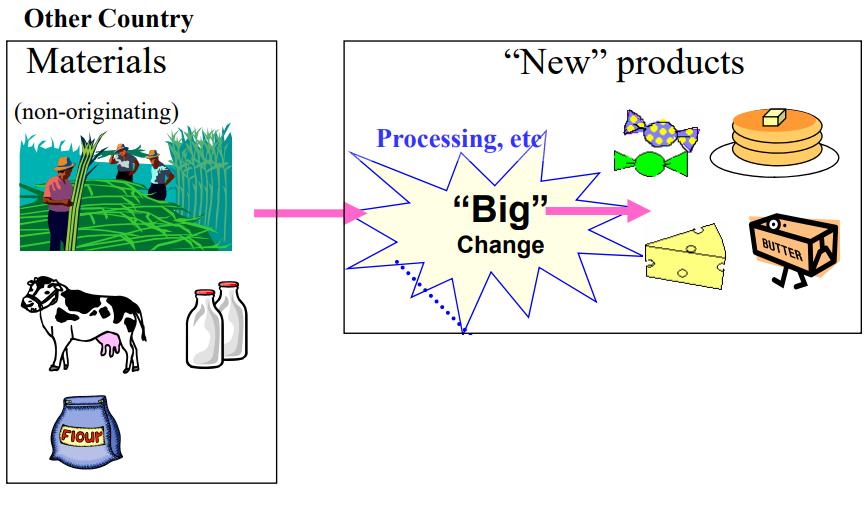
Retrieved from: Outline of Rules of Origin for EPA in Japan
This “Big change” is named as “substantial transformation” and a Party in which such a big change happened is considered as an origin of the Party.
Goods underwent big change are named as “Goods satisfied substantial transformation criterion”.
Change in Tariff Classification(CTC)
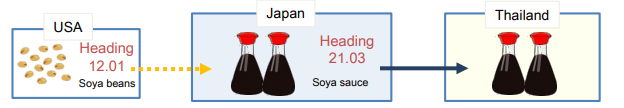
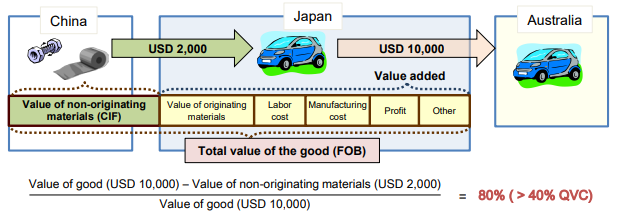
Qualifying/Regional Value Content(QVC or RVC)
Goods are considered as originating if a certain value (%) is added through
the production is undertaken in the territory of a party/country,
and the value-added exceeds the prescribed threshold (%).
(Example)
PSR for a passenger vehicle of heading 87.03 under Japan-Australia EPA:
the value added in the country of manufacture (Qualifying Value Content) is
not less than 40% and the last process of production has been performed in
the exporting party.
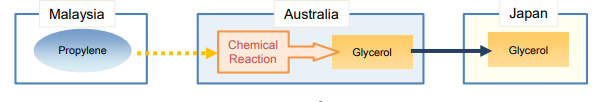
Specific manufacturing or Processing(SP)
Goods are considered as originating if the goods undergo specific manufacturing or
processing such as chemical reaction, distillation, purification, etc. in the territory of
a party/country.
(Example)
PSR for glycerol of subheading 2905.45 under Japan-Australia EPA:
the good has undergone a chemical reaction in the area of a party.
Chemical reaction is defined as a process which results in a molecule
with a newstructure.
Images retrieved from:Outline of Rules of Origin for EPA in Japan